Astragalus improves intestinal barrier function and immunity by acting on intestinal microbiota to treat T2DM: a research review
- PMID: 37638043
- PMCID: PMC10450032
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1243834
Astragalus improves intestinal barrier function and immunity by acting on intestinal microbiota to treat T2DM: a research review
Abstract
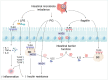
Diabetes is a significant chronic endocrine/metabolism disorder that can result in a number of life-threatening consequences. According to research, the gut microbiota is strongly linked to the development of diabetes, making it a viable target for diabetes treatment. The intestinal microbiota affects intestinal barrier function, organism immunity, and thus glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism. According to research, a disruption in the intestinal microbiota causes a decrease in short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), alters the metabolism of bile acids (BAs), branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and endotoxin secretion, resulting in insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and the progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Astragali Radix is a medicinal herb of the same genus as food that has been extensively researched for treating diabetes mellitus with promising results in recent years. Polysaccharides, saponins, flavonoids, and other components are important. Among them, Astragaloside has a role in protecting the cellular integrity of the pancreas and liver, can leading to alleviation of insulin resistance and reducing blood glucose and triglyceride (TC) levels; The primary impact of Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on diabetes is a decrease in insulin resistance, encouragement of islet cell proliferation, and suppression of islet β cell death; Astragali Radix flavonoids are known to enhance immunity, anti-inflammatory, regulate glucose metabolism and control the progression of diabetes. This study summarizes recent studies on Astragali Radix and its group formulations in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by modulating the intestinal microbiota.
Keywords: Astragali Radix; active ingredients; immunity; intestinal microbiota; metabolism; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2023 Su, Tang, Tang, Long, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Krummenauer MC, Bock MP, Leivas G, Martins FA, Ramalho R, Teló HG, et al. IDF21-0087 Metabolic interventions for diabetes treatment are associated with gut microbiota changes:a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract (2022) 186(S1):109460. doi: 10.1016/J.DIABRES.2022.109460 - DOI
-
- Nima M, Shabnam R, Zahra H, Mohammadreza K, Shahin B, Ali K, et al. Human gut microbiota and its possible relationship with obesity and diabetes. Int J Diabetes Develop Countries (2020) 41:235–43. doi: 10.1007/s13410-020-00881-w - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous