Dynamic analysis of rabies transmission and elimination in mainland China
- PMID: 37638210
- PMCID: PMC10458286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100615
Dynamic analysis of rabies transmission and elimination in mainland China
Abstract
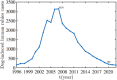
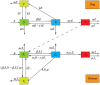
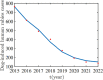
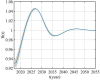
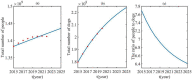
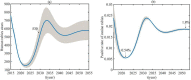
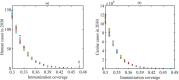
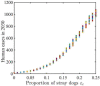
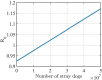
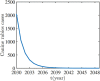
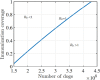
Rabies is an acute zoonotic infectious disease caused by rabies virus. In 2015, the World Health Organization proposed the goal of eliminating dog-induced human rabies by 2030. In response to this goal positively, China has been dedicated to the control and elimination of rabies mainly caused by dogs, for nearly 10 years. By applying infectious disease dynamics, in this paper, we establish a dog-human rabies transmission model to forecast future epidemic trends of rabies, assess whether the goal of eliminating dog-induced human rabies cases in China can be achieved in 2030, and further evaluate and suggest the follow-up sustained preventive measures after the elimination of human rabies. By analyzing and simulating above dynamic model, it is concluded that rabies has been well controlled in China in recent years, but dog-induced human rabies cannot be eliminated by 2030 according to current situation. In addition, we propose to improve rabies control efforts by increasing the immunization coverage rate of rural domestic dogs, controlling the number of stray dogs and preventing the import of rabies virus in wild animals. Immunization coverage rate of rural domestic dogs which is currently less than 10% is far from requirement, and it needs to reach 50%-60% to meet the goal of 2030. Since it is difficult to immunize stray dogs, we suggest to control the number of stray dogs below 15.27 million to achieve the goal. If the goal of eliminating human rabies is reached in 2030, the essential immunization coverage needs to be maintained for 18 years to reduce the number of canine rabies cases to zero. Lastly, to prevent transmission of rabies virus from wild animals to dogs, the thresholds of the number of dogs and the immunization coverage rate of dogs after eliminating canine rabies cases are also discussed.
Keywords: Dog-induced rabies; Dynamics; Elimination; Reproduction number; Stray dog population; Vaccination.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of rabies epidemics and the impact of control efforts in Guangdong Province, China.J Theor Biol. 2012 May 7;300:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Theor Biol. 2012. PMID: 22273729
-
Rabies Vaccination Targets for Stray Dog Populations.Front Vet Sci. 2017 Apr 13;4:52. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00052. eCollection 2017. Front Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28451589 Free PMC article.
-
Domestic dog demographics and estimates of canine vaccination coverage in a rural area of Zambia for the elimination of rabies.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Apr 28;15(4):e0009222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009222. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33909621 Free PMC article.
-
Dog rabies control in West and Central Africa: A review.Acta Trop. 2021 Dec;224:105459. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105459. Epub 2020 May 11. Acta Trop. 2021. PMID: 32404295 Review.
-
The Role of Dog Population Management in Rabies Elimination-A Review of Current Approaches and Future Opportunities.Front Vet Sci. 2017 Jul 10;4:109. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00109. eCollection 2017. Front Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28740850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology and Emerging Trends of Zoonotic Viral Diseases of Pigs in India.Viruses. 2025 Mar 6;17(3):381. doi: 10.3390/v17030381. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring one health-based strategies for rabies elimination: Overview and future prospects.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jun 18;19(6):e0013159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0013159. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40531916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiological characteristics of human rabies cases reported by sites in China from 2006 to 2022.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 13;24(1):966. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09864-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39272017 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of animal rabies in the Nizhny Novgorod region of Russia (2012-2022): the analysis of risk factors.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Oct 22;11:1440408. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1440408. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39502946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdulmajid S., Hassan A.S. Analysis of time delayed rabies model in human and dog populations with controls. Afr. Mat. 2021;32:1067–1085. doi: 10.1007/S13370-021-00882-W. - DOI
-
- Li J., Shi L., Wang Y., Cao S. Analysis strategies for rabies prevention and control in China. J. Appl. Virol. 2020;8:71–85. doi: 10.21092/JAV.V8I4.115. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

