Critical evaluation of kinetic schemes for coagulation
- PMID: 37639392
- PMCID: PMC10461854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290531
Critical evaluation of kinetic schemes for coagulation
Abstract
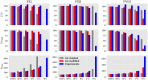
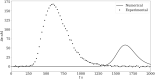
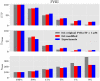
Two well-established numerical representations of the coagulation cascade either initiated by the intrinsic system (Chatterjee et al., PLOS Computational Biology 2010) or the extrinsic system (Butenas et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004) were compared with thrombin generation assays under realistic pathological conditions. Biochemical modifications such as the omission of reactions not relevant to the case studied, the modification of reactions related to factor XI activation and auto-activation, the adaptation of initial conditions to the thrombin assay system, and the adjustment of some of the model parameters were necessary to align in vitro and in silico data. The modified models are able to reproduce thrombin generation for a range of factor XII, XI, and VIII deficiencies, with the coagulation cascade initiated either extrinsically or intrinsically. The results emphasize that when existing models are extrapolated to experimental parameters for which they have not been calibrated, careful adjustments are required.
Copyright: © 2023 Ranc et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

