Environmental gradients reveal stress hubs pre-dating plant terrestrialization
- PMID: 37640935
- PMCID: PMC10505561
- DOI: 10.1038/s41477-023-01491-0
Environmental gradients reveal stress hubs pre-dating plant terrestrialization
Abstract
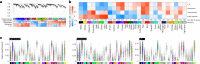
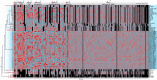
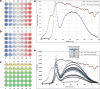
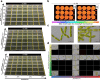
Plant terrestrialization brought forth the land plants (embryophytes). Embryophytes account for most of the biomass on land and evolved from streptophyte algae in a singular event. Recent advances have unravelled the first full genomes of the closest algal relatives of land plants; among the first such species was Mesotaenium endlicherianum. Here we used fine-combed RNA sequencing in tandem with a photophysiological assessment on Mesotaenium exposed to a continuous range of temperature and light cues. Our data establish a grid of 42 different conditions, resulting in 128 transcriptomes and ~1.5 Tbp (~9.9 billion reads) of data to study the combinatory effects of stress response using clustering along gradients. Mesotaenium shares with land plants major hubs in genetic networks underpinning stress response and acclimation. Our data suggest that lipid droplet formation and plastid and cell wall-derived signals have denominated molecular programmes since more than 600 million years of streptophyte evolution-before plants made their first steps on land.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








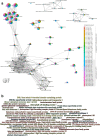
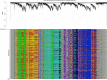
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 514060973/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SPP 2237/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- BU 2301/6-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- HO 2793/5-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- FE 446/14-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

