The Balance Between the Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of [177Lu]Lu-NeoB in a Preclinical Prostate Cancer Model
- PMID: 37640941
- PMCID: PMC10828073
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-023-01851-4
The Balance Between the Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of [177Lu]Lu-NeoB in a Preclinical Prostate Cancer Model
Abstract
Purpose: Radiolabeled NeoB is a promising gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR)-targeting radiopharmaceutical for theranostics of GRPR-expressing malignancies, e.g., prostate cancer (PCa). The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of different doses of [177Lu]Lu-NeoB on the balance between therapeutic efficacy and safety in a preclinical PCa model.
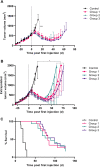
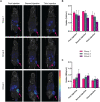
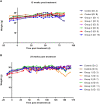
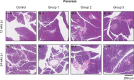
Procedures: To determine the efficacy of [177Lu]Lu-NeoB, PC-3 xenografted mice received 3 sham injections (control group) or 3 injections of 30 MBq/300 pmol, 40 MBq/400 pmol, or 60 MBq/600 pmol [177Lu]Lu-NeoB (groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively) 1 week apart. To quantify tumor uptake, single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) imaging was performed 4 h after the first, second, and third injection on a separate group of animals. For safety evaluations, pancreatic and renal tissues of non-tumor-bearing mice treated with the abovementioned [177Lu]Lu-NeoB doses were evaluated 12 and 24 weeks post-treatment.
Results: Treatment of PC-3 tumors with all three studied [177Lu]Lu-NeoB doses was effective. Median survival times were significantly (p < 0.0001) improved for treatment groups 1, 2, and 3 versus the control group (82 days, 89 days, 99 days versus 19 days, respectively). However, no significant differences were observed between treatment groups. Quantification of SPECT/CT images showed minimal differences in the average absolute radioactivity uptake, especially after the third injection. Histopathological analysis revealed no clear signs of treatment-related pancreatic toxicity. For the kidneys, atrophy and fibrosis were observed for one animal from group 1 and a chronic inflammatory response was observed for both animals from group 3 at 24 weeks post-treatment.
Conclusions: Treatment with [177Lu]Lu-NeoB is effective in a preclinical PCa model. Adjusting the administered dose could positively impact the risk-benefit balance as a higher dose might not lead to an increased therapeutic effect, but it may lead to an increase in toxicological effects in healthy organs such as the kidneys.
Keywords: Efficacy; Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR); Prostate cancer; Theranostics; Toxicity; [177Lu]Lu-NeoB.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Financial interests: F.O., D.B. and M.T. are employed by Advanced Accelerator Applications, a Novartis Company. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

