Discovery of novel JAK1 inhibitors through combining machine learning, structure-based pharmacophore modeling and bio-evaluation
- PMID: 37641144
- PMCID: PMC10464202
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04443-6
Discovery of novel JAK1 inhibitors through combining machine learning, structure-based pharmacophore modeling and bio-evaluation
Abstract
Background: Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) plays a critical role in most cytokine-mediated inflammatory, autoimmune responses and various cancers via the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Inhibition of JAK1 is therefore an attractive therapeutic strategy for several diseases. Recently, high-performance machine learning techniques have been increasingly applied in virtual screening to develop new kinase inhibitors. Our study aimed to develop a novel layered virtual screening method based on machine learning (ML) and pharmacophore models to identify the potential JAK1 inhibitors.
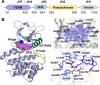
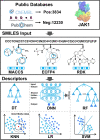
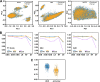
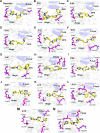
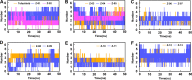
Methods: Firstly, we constructed a high-quality dataset comprising 3834 JAK1 inhibitors and 12,230 decoys, followed by establishing a series of classification models based on a combination of three molecular descriptors and six ML algorithms. To further screen potential compounds, we constructed several pharmacophore models based on Hiphop and receptor-ligand algorithms. We then used molecular docking to filter the recognized compounds. Finally, the binding stability and enzyme inhibition activity of the identified compounds were assessed by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and in vitro enzyme activity tests.
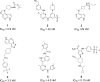
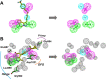
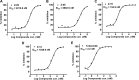
Results: The best performance ML model DNN-ECFP4 and two pharmacophore models Hiphop3 and 6TPF 08 were utilized to screen the ZINC database. A total of 13 potentially active compounds were screened and the MD results demonstrated that all of the above molecules could bind with JAK1 stably in dynamic conditions. Among the shortlisted compounds, the four purchasable compounds demonstrated significant kinase inhibition activity, with Z-10 being the most active (IC50 = 194.9 nM).
Conclusion: The current study provides an efficient and accurate integrated model. The hit compounds were promising candidates for the further development of novel JAK1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Janus kinase 1; Machine learning; Molecular dynamics simulations; Pharmacophore; Virtual screening.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Potent and Selective JAK1 Lead Compounds Through Ligand-Based Drug Design Approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 21;13:837369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.837369. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35529449 Free PMC article.
-
Putative dual inhibitors of Janus kinase 1 and 3 (JAK1/3): Pharmacophore based hierarchical virtual screening.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Oct;76:109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29990790
-
Pharmacophore modeling of JAK1: A target infested with activity-cliffs.J Mol Graph Model. 2020 Sep;99:107615. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2020.107615. Epub 2020 Apr 21. J Mol Graph Model. 2020. PMID: 32339898
-
Searching for Novel Janus Kinase-2 Inhibitors Using a Combination of Pharmacophore Modeling, 3D-QSAR Studies and Virtual Screening.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(3):268-294. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160919163930. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27659251 Review.
-
Pharmacophore modeling in drug design.Adv Pharmacol. 2025;103:313-324. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2025.01.010. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Adv Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40175047 Review.
Cited by
-
An integrated approach for novel PTP1B inhibitor screening: combining machine learning models, molecular docking, molecular and dynamics simulations.Mol Divers. 2025 Jul 21. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11292-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40690114
-
Integrated machine learning and deep learning-based virtual screening framework identifies novel natural GSK-3β inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2025 Jul 16;39(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s10822-025-00637-w. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2025. PMID: 40668407
-
Construction of IRAK4 inhibitor activity prediction model based on machine learning.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug;28(4):2289-2300. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10926-5. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38970641 Review.
-
Discovery of novel VEGFR2 inhibitors against non-small cell lung cancer based on fingerprint-enhanced graph attention convolutional network.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 3;22(1):1097. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05893-2. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39627783 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

