Vagus nerve stimulation-induced stromal cell-derived factor-l alpha participates in angiogenesis and repair of infarcted hearts
- PMID: 37641543
- PMCID: PMC10682864
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14475
Vagus nerve stimulation-induced stromal cell-derived factor-l alpha participates in angiogenesis and repair of infarcted hearts
Abstract
Aims: We aim to explore the role and mechanism of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in coronary endothelial cells and angiogenesis in infarcted hearts.
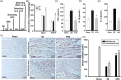
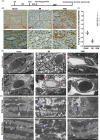
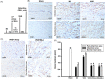
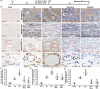
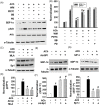
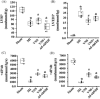
Methods and results: Seven days after rat myocardial infarction (MI) was prepared by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery, the left cervical vagus nerve was treated with electrical stimulation 1 h after intraperitoneal administration of the α7-nicotinic acetylcholine inhibitor mecamylamine or the mAChR inhibitor atropine or 3 days after local injection of Ad-shSDF-1α into the infarcted heart. Cardiac tissue acetylcholine (ACh) and serum ACh, tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels were detected by ELISA to determine whether VNS was successful. An inflammatory injury model in human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) was established by lipopolysaccharide and identified by evaluating TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels and tube formation. Immunohistochemistry staining was performed to evaluate CD31-positive vessel density and stromal cell-derived factor-l alpha (SDF-1α) expression in the MI heart in vivo and the expression and distribution of SDF-1α, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 and CXCR7 in HCAECs in vitro. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of SDF-1α, V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog (AKT), phosphorylated AKT (pAKT), specificity protein 1 (Sp1) and phosphorylation of Sp1 in HCAECs. Left ventricular performance, including left ventricular systolic pressure, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and rate of the rise and fall of ventricular pressure, should be evaluated 28 days after VNS treatment. VNS was successfully established for MI therapy with decreases in serum TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels and increases in cardiac tissue and serum ACh levels, leading to increased SDF-1α expression in coronary endothelial cells of MI hearts, triggering angiogenesis of MI hearts with increased CD31-positive vessel density, which was abolished by the m/nAChR inhibitors mecamylamine and atropine or knockdown of SDF-1α by shRNA. ACh promoted SDF-1α expression and its distribution along with the branch of the formed tube in HCAECs, resulting in an increase in the number of tubes formed in HCAECs. ACh increased the levels of pAKT and phosphorylation of Sp1 in HCAECs, resulting in inducing SDF-1α expression, and the specific effects could be abolished by mecamylamine, atropine, the PI3K/AKT blocker wortmannin or the Sp1 blocker mithramycin. Functionally, VNS improved left ventricular performance, which could be abolished by Ad-shSDF-1α.
Conclusions: VNS promoted angiogenesis to repair the infarcted heart by inducing SDF-1α expression and redistribution along new branches during angiogenesis, which was associated with the m/nAChR-AKT-Sp1 signalling pathway.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Myocardial infarction; SDF-1α; Sp1; Vagal nerve stimulation.
© 2023 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
VNS improves VSMC metabolism and arteriogenesis in infarcted hearts through m/n-AChR-Akt-SDF-1α in adult male rats.J Mol Histol. 2024 Feb;55(1):51-67. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10171-4. Epub 2024 Jan 2. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 38165566 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-A and VEGF-B Coordinate the Arteriogenesis to Repair the Infarcted Heart with Vagus Nerve Stimulation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(2):433-449. doi: 10.1159/000491775. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30016789
-
Mesenchymal stem cells over-expressing SDF-1 promote angiogenesis and improve heart function in experimental myocardial infarction in rats.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009 Oct;36(4):644-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.04.052. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19524448
-
Stromal derived factor 1α: a chemokine that delivers a two-pronged defence of the myocardium.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Sep;143(3):305-15. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24704323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No consistent evidence for the anti-inflammatory effect of vagus nerve stimulation in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Feb;116:237-258. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.12.008. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Brain Behav Immun. 2024. PMID: 38070618
Cited by
-
Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Alleviates Monobenzone-Induced Vitiligo in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 18;25(6):3411. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063411. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542385 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress in myocardial function and diseases related to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jun;55(6):86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5527. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40183403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycolipid Metabolic Disorders, Metainflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling Pathways.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 12;13(7):519. doi: 10.3390/biology13070519. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: an innovative strategy for treating diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 4;52(1):199. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10288-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39903351 Review.
References
-
- Li P, Liu H, Sun P, Wang X, Wang C, Wang L, Wang T. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation attenuates vascular endothelial impairments and reduces the inflammatory profile via inhibition of the NF‐κB signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Exp Gerontol. 2016; 74: 43–55. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Zheng C, Sato T, Kawada T, Sugimachi M, Sunagawa K. Vagal nerve stimulation markedly improves long‐term survival after chronic heart failure in rats. Circulation. 2004; 109: 120–124. - PubMed
-
- Shen MJ, Shinohara T, Park HW, Frick K, Ice DS, Choi EK, Han S, Maruyama M, Sharma R, Shen C, Fishbein MC, Chen LS, Lopshire JC, Zipes DP, Lin SF, Chen PS. Continuous low level vagus nerve stimulation reduces stellate ganglion nerve activity and paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmias in ambulatory canines. Circulation. 2011; 123: 2204–2280. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niccoli G, Scalone G, Lerman A, Crea F. Coronary microvascular obstruction in acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37: 1024–1040. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

