Admission blood pressure and clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischaemic stroke treated with intravenous alteplase and endovascular treatment versus endovascular treatment alone: A MR CLEAN-NO IV substudy
- PMID: 37641554
- PMCID: PMC10472956
- DOI: 10.1177/23969873231173274
Admission blood pressure and clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischaemic stroke treated with intravenous alteplase and endovascular treatment versus endovascular treatment alone: A MR CLEAN-NO IV substudy
Abstract
Introduction: High systolic blood pressure (SBP) is associated with poor functional outcome. We analysed whether the association of SBP with outcomes after endovascular treatment (EVT) is modified by prior intravenous thrombolysis (IVT).
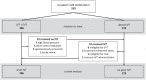
Patients and methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of MR CLEAN-NO IV, a randomised trial of IVT with alteplase followed by EVT versus EVT alone, within 4.5 h from stroke onset. SBP was recorded on hospital admission. The primary outcome was 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score and secondary outcomes included symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage (sICH) and successful reperfusion (eTICI 2b-3), analysed with (ordinal) logistic regression. Estimates were calculated per 10 mmHg change in SBP. We assessed whether IVT modified the associations of SBP with these outcomes using multiplicative interaction terms.
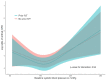
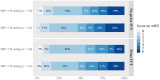
Results: Of 539 randomised patients, 266 received IVT. The association of SBP with mRS score was J-shaped, with an inflection point at 150 mmHg. Using 150 mmHg as a reference point, SBPs higher than 150 mmHg were associated with poor functional outcome (acOR: 1.23, 95% CI: 1.09-1.38), but lower SBPs were not (acOR: 1.14, 95% CI: 0.99-1.30). Higher SBP was not associated with the risk of sICH (aOR: 1.09, 95% CI: 0.93-1.27) nor with the probability of successful reperfusion (aOR: 1.00, 95% CI: 0.91-1.10). Our main result was that we found no effect modification by IVT (p-values for interaction, mRS = 0.94; sICH = 0.26; successful reperfusion = 0.58).
Discussion and conclusion: There was no effect modification of IVT with SBP for any of the clinical outcomes. Therefore, the level of SBP (if ⩽185/110 mmHg) should not guide IVT decisions in patients otherwise eligible for both IVT and EVT within the 4.5-h time window.
Trial registration: ISRCTN80619088, https://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN80619088.
Keywords: Blood pressure; acute ischaemic stroke; alteplase; endovascular treatment; hypertension; intravenous thrombolysis; randomised controlled trial; thrombectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: AP reports an institutional grant by Siemens Healthineers. CM reports funding from CVON/Dutch Heart Foundation and Stryker (related to this project) and funding from European Commission, Healthcare Evaluation Netherlands TWIN Foundation (unrelated to this project), all paid to institution, and is shareholder of Nicolab. DD reports funding from the Dutch Heart Foundation, Brain Foundation Netherlands, The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development, Health Holland Top Sector Life Sciences & Health, and unrestricted grants from Penumbra Inc., Stryker, Medtronic, Thrombolytic Science, LLC and Cerenovus for research, all paid to institution. HW reports funding from Stryker, paid to the CONTRAST consortium, and consultation fees from Bayer and LivaNova, paid to his institution. JC reports funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer and Portola, all to fund medical research and paid to his institution. PN reports funding from Stryker, paid to the CONTRAST consortium. YR is minor shareholder of Nicolab. All other authors report no conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Intravenous Alteplase Treatment on First-Line Stent Retriever Versus Aspiration Alone During Endovascular Treatment.Stroke. 2022 Nov;53(11):3278-3288. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.038390. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Stroke. 2022. PMID: 35876018 Clinical Trial.
-
Hemorrhage rates in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous alteplase and thrombectomy versus thrombectomy alone.J Neurointerv Surg. 2023 Nov;15(e2):e262-e269. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2022-019569. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023. PMID: 36396434 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of time metrics on the treatment effect of intravenous alteplase prior to endovascular treatment in MR CLEAN-NO IV.J Neurointerv Surg. 2023 Sep;15(e1):e54-e59. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2022-018998. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023. PMID: 35831176
-
Efficacy and safety of endovascular treatment with or without intravenous alteplase in acute anterior circulation large vessel occlusion stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Neurol Sci. 2022 Jun;43(6):3551-3563. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06017-8. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35314911 Review.
-
Endovascular thrombectomy without versus with different pre-intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1344961. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1344961. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38348167 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hemorrhagic Coagulation Disorders and Ischemic Stroke: How to Reconcile Both?Neurol Int. 2023 Nov 30;15(4):1443-1458. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15040093. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 38132972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multicenter trial on the predictors of different subtypes of hemorrhagic infarction after thrombolysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 30;14(1):29822. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76189-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39616189 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome Predictor Differences in Infratentorial and Supratentorial Ischemic Stroke.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 10;15(4):633. doi: 10.3390/life15040633. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283187 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial Hemorrhage in Patients With Stroke After Endovascular Treatment With or Without IV Alteplase: An Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis.JAMA Neurol. 2025 Aug 11:e252610. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2025.2610. Online ahead of print. JAMA Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40788598
-
Big data analysis of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke: a study based on bibliometric analysis.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024 Oct;82(10):1-13. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1789228. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 39216487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vemmos KN, Tsivgoulis G, Spengos K, et al.. U-shaped relationship between mortality and admission blood pressure in patients with acute stroke. J Intern Med 2004; 255: 257–265. - PubMed
-
- Leonardi-Bee J, Bath PM, Phillips SJ, et al.. Blood pressure and clinical outcomes in the International Stroke Trial. Stroke 2002; 33: 1315–1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

