Nature-inspired nanocarriers for improving drug therapy of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 37641591
- PMCID: PMC10460486
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbad069
Nature-inspired nanocarriers for improving drug therapy of atherosclerosis
Abstract
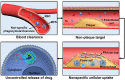
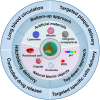
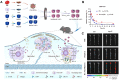
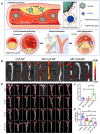
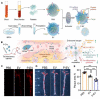
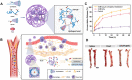
Atherosclerosis (AS) has emerged as one of the prevalent arterial vascular diseases characterized by plaque and inflammation, primarily causing disability and mortality globally. Drug therapy remains the main treatment for AS. However, a series of obstacles hinder effective drug delivery. Nature, from natural micro-/nano-structural biological particles like natural cells and extracellular vesicles to the distinctions between the normal and pathological microenvironment, offers compelling solutions for efficient drug delivery. Nature-inspired nanocarriers of synthetic stimulus-responsive materials and natural components, such as lipids, proteins and membrane structures, have emerged as promising candidates for fulfilling drug delivery needs. These nanocarriers offer several advantages, including prolonged blood circulation, targeted plaque delivery, targeted specific cells delivery and controlled drug release at the action site. In this review, we discuss the nature-inspired nanocarriers which leverage the natural properties of cells or the microenvironment to improve atherosclerotic drug therapy. Finally, we provide an overview of the challenges and opportunities of applying these innovative nature-inspired nanocarriers.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; drug delivery; membrane-coating; nature-inspired nanocarriers; stimuli-responsive.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang S, Liu Y, Cao Y, Zhang S, Sun J, Wang Y, Song S, Zhang H.. Targeting the microenvironment of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques: an emerging diagnosis and therapy strategy for atherosclerosis. Adv Mater 2022;34:e2110660. - PubMed
-
- Song P, Fang Z, Wang H, Cai Y, Rahimi K, Zhu Y, Fowkes FGR, Fowkes FJI, Rudan I.. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Glob Health 2020;8:e721–9. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature 2021;592:524–33. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

