Recurrent Subdural Hematoma: An Institutional Experience
- PMID: 37641767
- PMCID: PMC10460295
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42582
Recurrent Subdural Hematoma: An Institutional Experience
Abstract
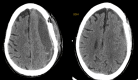
Background Chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) is a common neurosurgical problem, which offers a good outcome following surgery. In many cases, burr hole irrigation and drainage under local anesthesia can provide satisfactory results. However, recurrence can be a cause for concern for both the surgeon and the patient. While recurrence is not a frequent phenomenon, studies have reported rates of up to 31.6%. Aims and objectives In this study, our objective is to examine a comprehensive range of potential risk factors and provide valuable insights into identifying patients at a higher risk of recurrence to aid in surgical decision-making. Methodology This study employed a prospective and retrospective design, conducted between 2017 and 2021, at Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research. The study received ethical approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee. The research aimed to assess patients who underwent surgery for CSDH, with a particular focus on those who experienced recurrence. Results The average age of patients with recurrence was 71.5 years compared to 65.2 years in the no-recurrence group, but this difference did not show a significant statistical correlation. A significant male predominance was observed, with 27 men and four women affected (out of a total of 147 men and 73 women in the study), resulting in a statistically significant p-value of 0.01. On multivariate analysis, heterogenous subtypes were a significant predictor of recurrence (OR: 8.88, 95% CI: 6.96-16.54, p = 0.01). The mean midline shift in those with recurrence was 11.4 mm compared to 7.09 mm in those without recurrence. This was a statistically significant correlation with a p-value of 0.02. Regarding those with recurrence, 24 patients underwent evacuation using two burr holes, with one placed in the frontal region and another in the parietal region. All of these patients had a subdural drain placed, which was removed on postoperative day 2. The remaining eight patients underwent a mini-craniotomy for evacuation. We had four cases of refractory CSDH, all of whom underwent the second evacuation using burr holes. Three of them underwent evacuation via craniotomy, while the family of the fourth patient did not give consent for the procedure. Conclusion Patient-related factors such as gender, bilateral presentation, and the presence of hypertension and radiological factors such as the presence of heterogenous subtype and a significant midline shift are clues toward a higher chance of recurrence.
Keywords: burr hole drainage; ct prediction; open craniotomy; recurrence rate; subdural hematoma.
Copyright © 2023, Swamiyappan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Chronic subdural haematoma in elderly patients: a retrospective analysis of 322 patients between the ages of 65-94 years. Borger V, Vatter H, Oszvald Á, Marquardt G, Seifert V, Güresir E. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2012;154:1549–1554. - PubMed
-
- Chronic subdural hematoma: surgical treatment and outcome in 104 patients. Ernestus RI, Beldzinski P, Lanfermann H, Klug N. Surg Neurol. 1997;48:220–225. - PubMed
-
- Surgical treatment of chronic subdural hematoma in 500 consecutive cases: clinical characteristics, surgical outcome, complications, and recurrence rate. Mori K, Maeda M. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2001;41:371–381. - PubMed
-
- Risk factors for reoperation after initial burr hole trephination in chronic subdural hematomas. Schwarz F, Loos F, Dünisch P, Sakr Y, Safatli DA, Kalff R, Ewald C. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;138:66–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources