N-retinylidene- N-retinylethanolamine degradation in human retinal pigment epithelial cells via memantine- and ifenprodil-mediated autophagy
- PMID: 37641807
- PMCID: PMC10466070
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.449
N-retinylidene- N-retinylethanolamine degradation in human retinal pigment epithelial cells via memantine- and ifenprodil-mediated autophagy
Abstract
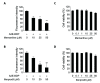
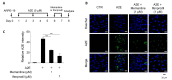
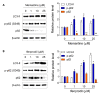
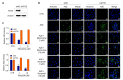
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are ionic glutamine receptors involved in brain development and functions such as learning and memory formation. NMDA receptor inhibition is associated with autophagy activation. In this study, we investigated whether the NMDA receptor antagonists, memantine and ifenprodil, induce autophagy in human retinal pigment epithelial cells (ARPE-19) to remove Nretinylidene- N-retinylethanolamine (A2E), an intracellular lipofuscin component. Fluorometric analysis using labeled A2E (A2E-BDP) and confocal microscopic examination revealed that low concentrations of NMDA receptor antagonists, which did not induce cytotoxicity, significantly reduced A2E accumulation in ARPE-19 cells. In addition, memantine and ifenprodil activated autophagy in ARPE-19 cells as measured by microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain3-II formation and phosphorylated p62 protein levels. Further, to understand the correlation between memantine- and ifenprodil-mediated A2E degradation and autophagy, autophagy-related 5 (ATG5) was depleted using RNA interference. Memantine and ifenprodil failed to degrade A2E in ARPE-19 cells lacking ATG5. Taken together, our study indicates that the NMDA receptor antagonists, memantine and ifenprodil, can remove A2E accumulated in cells via autophagy activation in ARPE-19 cells.
Keywords: A2E; ARPE-19; Autophagy; Ifenprodil; Memantine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yau SY, Bettio L, Vetrici M, Truesdell A, Chiu C, Chiu J, Truesdell E, Christie BR. Chronic minocycline treatment improves hippocampal neuronal structure, NMDA receptor function, and memory processing in Fmr1 knockout mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2018;113:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.01.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Korinek M, Kapras V, Vyklicky V, Adamusova E, Borovska J, Vales K, Stuchlik A, Horak M, Chodounska H, Vyklicky L., Jr Neurosteroid modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors: molecular mechanism and behavioral effects. Steroids. 2011;76:1409–1418. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2011.09.002. - DOI - PubMed

