Kinesin superfamily member 15 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 37641808
- PMCID: PMC10466069
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.457
Kinesin superfamily member 15 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
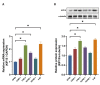
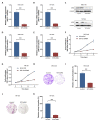
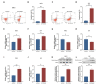
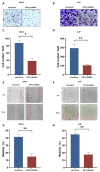
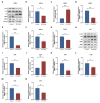
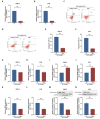
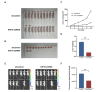
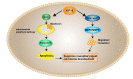
The aim of this study was to investigate the role of kinesin superfamily member 15 (KIF15) in nasopharyngeal carcinogenesis (NPC) and explore its underlying mechanisms. We employed various assays, including the CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry, the Transwell and scratch assay, Western blotting, and nude mice transplantation tumor, to investigate the impact of KIF15 on NPC. Our findings demonstrate that KIF15 plays a critical role in the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of NPC cells. Furthermore, we discovered that silencing KIF15 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion while promoting apoptosis, and that KIF15's effect on NPC cell growth is mediated through the PI3K/AKT and P53 signaling pathways. Additionally, we showed that KIF15 promotes nasopharyngeal cancer cell growth in vivo. Our study sheds light on the significance of KIF15 in NPC by revealing that KIF15 knockdown inhibits NPC cell growth through the regulation of AKT-related signaling pathways. These findings suggest that KIF15 represents a promising therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of NPC.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; Kinesins; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tang SQ, Mao YP, Xu C, Guo R, Li WF, Tang LL, Sun Y, Ma J. The evolution of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging system over a 10-year period: implications for future revisions. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020;133:2044–2053. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000978.45b20d7da1104cda981fe16dd2ef952e - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hung CC, Tu MY, Chien TW, Lin CY, Chow JC, Chou W. The model of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics on 100 top-cited articles of nasopharyngeal carcinoma from 2013 to 2022: bibliometric analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023;102:e32824. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

