Inhibition of the interaction between Hippo/YAP and Akt signaling with ursolic acid and 3'3-diindolylmethane suppresses esophageal cancer tumorigenesis
- PMID: 37641811
- PMCID: PMC10466072
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.493
Inhibition of the interaction between Hippo/YAP and Akt signaling with ursolic acid and 3'3-diindolylmethane suppresses esophageal cancer tumorigenesis
Abstract
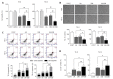
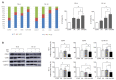
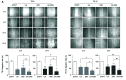
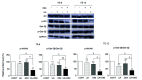
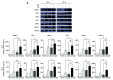
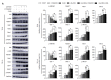
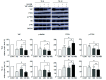
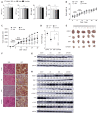
Hippo/YAP signaling hinders cancer progression. Inactivation of this pathway contributes to the development of esophageal cancer by activation of Akt. However, the possible interaction between Akt and Hippo/YAP pathways in esophageal cancer progression is unclear. In this study, we found that ursolic acid (UA) plus 3'3-diindolylmethane (DIM) efficiently suppressed the oncogenic Akt/Gsk-3β signaling pathway while activating the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway in esophageal cancer cells. Moreover, the addition of the Akt inhibitor LY294002 and the PI3K inhibitor 3-methyladenine enhanced the inhibitory effects of UA plus DIM on Akt pathway activation and further stimulated the Hippo pathway, including the suppression of YAP nuclear translocation in esophageal cancer cells. Silencing YAP under UA plus DIM conditions significantly increased the activation of the tumor suppressor PTEN in esophageal cancer cells, while decreasing p-Akt activation, indicating that the Akt signaling pathway could be down-regulated in esophageal cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Furthermore, in a xenograft nude mice model, UA plus DIM treatment effectively diminished esophageal tumors by inactivating the Akt pathway and stimulating the Hippo signaling pathway. Thus, our study highlights a feedback loop between the PI3K/Akt and Hippo signaling pathways in esophageal cancer cells, implying that a low dose of UA plus DIM could serve as a promising chemotherapeutic combination strategy in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Keywords: 3′,3-diindolylmethane; Akt; Esophageal squamous cancer cells; Hippo signaling pathway; Ursolic acid; YAP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Inhibition of colorectal cancer tumorigenesis by ursolic acid and doxorubicin is mediated by targeting the Akt signaling pathway and activating the Hippo signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Jan;27(1):11. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12898. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36382656 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN lipid phosphatase inactivation links the hippo and PI3K/Akt pathways to induce gastric tumorigenesis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 22;37(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0795-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30134988 Free PMC article.
-
Activating Hippo Pathway via Rassf1 by Ursolic Acid Suppresses the Tumorigenesis of Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 23;20(19):4709. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194709. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31547587 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting YAP and Hippo signaling pathway in liver cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Aug;14(8):855-68. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.499361. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20545481 Review.
-
Targeting the Hippo Signaling Pathway for Tissue Regeneration and Cancer Therapy.Genes (Basel). 2016 Aug 30;7(9):55. doi: 10.3390/genes7090055. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27589805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of 6'-Sialyllactose on LPS-induced macrophage inflammation via regulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling pathways.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 1;28(6):503-513. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.6.503. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39467714 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

