Antibiotic waste in a pediatric healthcare system: Wasting drugs that are in limited supply
- PMID: 37642014
- PMCID: PMC10877531
- DOI: 10.1017/ice.2023.118
Antibiotic waste in a pediatric healthcare system: Wasting drugs that are in limited supply
Abstract
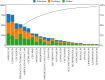
In a pediatric hospital system over 2 years, 58,607 doses of antibiotic were wasted, an average of 80 doses per day, including drugs in shortage nationwide. Approximately 50% of waste occurred within the first 2 days of admission or the day of discharge, with ampicillin being the most wasted drug (N = 7,789 doses).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Singh H, Eckelman M, Berwick DM, Sherman JD. Mandatory reporting of emissions to achieve net-zero health care. N Engl J Med 2022;387:2469–2476. - PubMed
-
- Quadri F, Mazer-Amirshahi M, Fox ER, et al. Antibacterial drug shortages from 2001 to 2013: implications for clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:1737–1742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical