Triggering of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Tannic Acid Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 37642057
- PMCID: PMC10685243
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.8.2705
Triggering of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Tannic Acid Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
Introduction: Due to the pivotal role of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in cancers, interfering with its function can cause the accumulation of unfolded proteins, which ultimately leads to the activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathway and apoptosis. Therefore, the use of plant compounds such as tannic acid with UPR-inducing properties can be proposed as a possible treatment method for cancer. In this study, we investigated the effect of tannic acid on cell migration, colony formation, growth, and UPR-induced apoptosis in the SW48 colorectal cancer cell line.
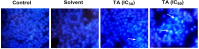
Methods: The MTT assay was performed to investigate the cytotoxic effect of tannic acid. We performed the qPCR method to elucidate the effect of tannic acid on the expression of Bim, MMP-9, Bcl-xL, cyclin D1, CHOP, and ATF4 genes. We also used the colony formation and migration experiments to investigate the effect of this compound on the colony formation and migration ability of tumor cells. Finally, we used Hoechst staining to measure cell apoptosis.
Results: Tannic acid inhibited the cell survival, clonogenic, and migration of colon cancer cells. This compound increased the expression of ER stress-mediated UPR genes, ATF4 and CHOP. Moreover; tannic acid increased the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins like Bim, while at the same time causing a sharp decline in the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL. A decline in MMP-9 expression confirmed the anti-metastatic role of this compound.
Conclusion: Taken together, tannic acid can induce apoptosis via ER stress-mediated UPR pathway, and has a suppressive effect on cell viability, growth, migration, colony formation, and metastasis, suggesting it may be a potential drug in colorectal cancer treatment.
Keywords: ATF4; CHOP; Endoplasmic reticulum; Tannic acid; colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare
Figures




Similar articles
-
Induction of Unfolded Protein Response by Tannic Acid Triggers Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jun 1;24(6):2029-2035. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.6.2029. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37378933 Free PMC article.
-
Tannic Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 7;10(3):68. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030068. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29518944 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of fatty acids on inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Sep;103(9):8643-8654. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-18080. Epub 2020 Jul 1. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32622599
-
The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(6):533-44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27211800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the ER-induced UPR pathway, apoptosis, and autophagy in colorectal cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154706. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154706. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37499516 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Plant-Derived Polyphenols on Combating Efflux-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 24;26(9):4030. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094030. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physicochemical, Volatile Compound Profile, Antioxidant, and Cytotoxic Activities of Northeastern Thai Ethnic Ready-to-Serve Food Pastes Jaew Hon and Gang Om: A Comparative Study of Laboratory and Industrial Production Processes.Foods. 2025 Mar 4;14(5):876. doi: 10.3390/foods14050876. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077580 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal activity of tannic acid against Candida spp. and its mechanism of action.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Dec;55(4):3679-3690. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01477-w. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39179891 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Invasion: The Role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):35. doi: 10.3390/biom15010035. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darvin P, Baeg SJ, Joung YH, et al. Tannic acid inhibits the Jak2/STAT3 pathway and induces G1/S arrest and mitochondrial apoptosis in YD-38 gingival cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:1111–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

