NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 play a role in atherosclerosis and chronic stress
- PMID: 37642954
- PMCID: PMC10496984
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204947
NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 play a role in atherosclerosis and chronic stress
Abstract
Objective: Atherosclerosis is characterized by the formation of fibrofatty plaques in the intima of arteries, resulting in thickening of the vessel wall and narrowing of the lumen. Chronic stress refers to individuals in a state of long-term chronic stress. However, the relationship between NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 and atherosclerosis and chronic stress is unclear.
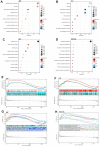
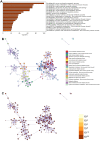
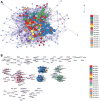
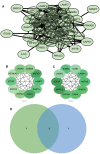
Method: The atherosclerosis with chronic stress group data file was used. DEGs were screened and WGCNA was performed. Construction and analysis of PPI Network. Functional enrichment analysis, GSEA, gene expression heatmap, immune infiltration analysis and mRNA analysis were performed. CTD was used to find diseases most related to core genes. WB was performed. TargetScan was used to screen miRNAs of DEGs.
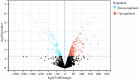
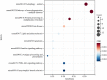
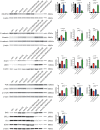
Results: 1708 DEGs were identified. According to GO analysis, they were mainly enriched in catabolic processes, organic acid metabolism processes, carboxylic acid metabolism processes. KEGG analysis showed that they were mainly enriched in metabolic pathways, fatty acid metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway, glycolysis / gluconeogenesis, fructose and mannose metabolism. Gene expression heatmap showed that the core genes (NDUFB11, NDUFS3) were lowly expressed in samples of those with atherosclerosis accompanied by chronic stress and highly expressed in the normal samples. NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 were associated with necrosis, hyperplasia, inflammation, renal disease, weight loss, memory impairment, and cognitive impairment. WB showed that the expression level of NDUFS3 in atherosclerosis and chronic stress was lower than that in control group.
Conclusions: NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 are underexpressed in atherosclerosis and chronic stress; the lower NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 levels, the worse the prognosis.
Keywords: NDUFB11; NDUFS3; atherosclerosis; bioinformatics; chronic stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
NDUFB11 and NDUFS3 regulate arterial atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis: Potential markers of atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e36133. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036133. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986300 Free PMC article.
-
Association of abnormal NDUFB2 and UQCRH expression with venous thromboembolism in patients with liver cirrhosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jan 5;103(1):e36868. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036868. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38181234 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of NADH Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit B11 induces catheter-associated venous thrombosis on continuous blood purification.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36520. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036520. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050233 Free PMC article.
-
CEACAM1 as a molecular target in oral cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Aug 16;15(16):8137-8154. doi: 10.18632/aging.204960. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37589542 Free PMC article.
-
CALM3 affects the prognosis of leukemia and hemorrhoids.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 3;102(44):e36027. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036027. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37932969 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Puerarin Improves Cancer-Induced Bone Pain by Recovering Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Spinal Cord.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 10;20(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10224-3. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40493135
-
Identification of markers correlating with mitochondrial function in myocardial infarction by bioinformatics.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 30;19(12):e0316463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316463. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39775580 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of signature genes related to fetoplacental vascular endothelial cell programming in gestational diabetes mellitus using bioinformatics analysis.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 14;16:1600756. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1600756. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40727584 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying molecular subgroups of patients with preeclampsia through bioinformatics.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jun 3;11:1367578. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1367578. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38887449 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

