Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis
- PMID: 37643301
- PMCID: PMC11397906
- DOI: 10.1089/can.2023.0025
Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis
Abstract
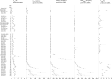
Background: In this review, we provide an updated assessment of available evidence on the pharmacokinetics (PK) of CBD and explore the impact of different factors on PK outcomes. Materials and Methods: This systematic review and meta-regression analysis was preregistered (PROSPERO: CRD42021269857). We systematically searched Medline, Embase, PsycInfo, and Web of Science Core Collection up to November 19, 2022. Trials of CBD in healthy adults were included if they reported at least one of the PK parameters of interest, including Tmax, Cmax, AUC0-t, AUC0-inf, and T1/2, in serum or plasma. Studies of patient populations or CBD co-administration with other medications were excluded. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Quality Assessment Tool for Before-After Studies with no Control Group was used. Random-effects multivariable meta-regression analysis was conducted. Results: A total of 112 trial arms from 39 studies were included; 26 trial arms had a "Good" quality, 70 "Fair," and 16 "Poor." Eight arms used inhalation CBD, 29 oromucosal, 73 oral, and 2 intravenous. CBD formulations could be categorized to nanotech (n=14), oil-based (n=21), alcohol-based (n=10), water-based (n=12), Sativex (n=17), and Epidiolex® (n=22). For single-dose studies, CBD doses ranged between 2 and 100 mg in inhalation, 5-50 mg in oromucosal, and 0.42-6000 mg in oral administration. Sixty-six trial arms had only male participants or a higher number of male than female participants. The duration of the PK session was between 4 and 164 h. A higher CBD dose was associated with higher Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-inf. Compared with oral administration, oromucosal administration was associated with lower Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-inf. Fed status was associated with higher Cmax and AUC0-t when compared with the fasting status. A higher ratio of female participants was associated with lower Tmax in oral administration and higher Cmax. Conclusion: As expected, CBD dose, route of administration, and diet were major determinants of CBD PK with oral routes providing higher bioavailability and nanotechnology formulations a faster onset. Although CBD appeared to have a faster onset and longer duration in women, more studies are required to delineate the role of biological sex. Factors that influence CBD PK have implications for medication development and appropriate dosing in clinical practice.
Keywords: CBD; bioavailability; cannabis; clinical trials; pharmacokinetics.
Figures
Update of
-
Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 2:2023.02.01.23285341. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.01.23285341. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024 Aug;9(4):939-966. doi: 10.1089/can.2023.0025. PMID: 36778355 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- VanDolah HJ, Bauer BA, Mauck KF. Clinicians' Guide to Cannabidiol and Hemp Oils. Mayo Clin Proc 2019;94(9):1840–1851. - PubMed
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence. Cannabidiol (CBD) Critical Review Report. Fortieth Meeting, Geneva, June 4–7, 2018.
-
- Julious SA, Debarnot CA. Why are pharmacokinetic data summarized by arithmetic means? J Biopharm Stat 2000;10(1):55–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials