Pan-cancer Analysis Reveals Cancer-dependent Expression of SOX17 and Associated Clinical Outcomes
- PMID: 37643784
- PMCID: PMC10464944
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20395
Pan-cancer Analysis Reveals Cancer-dependent Expression of SOX17 and Associated Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
Background/aim: SRY-box containing gene 17 (SOX17) plays a pivotal role in cancer onset and progression and is considered a potential target for cancer diagnosis and treatment. However, the expression pattern of SOX17 in cancer and its clinical relevance remains unknown. Here, we explored the relationship between the expression of SOX17 and drug response by examining SOX17 expression patterns across multiple cancer types.
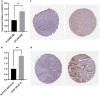
Materials and methods: Single-cell and bulk RNA-seq analyses were used to explore the expression profile of SOX17. Analysis results were verified with qPCR and immunohistochemistry. Survival, drug response, and co-expression analyses were performed to illustrate its correlation with clinical outcomes.
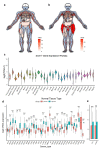
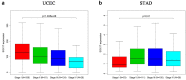
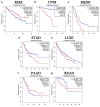
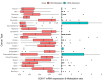
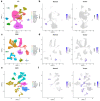
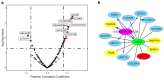
Results: The results revealed that abnormal expression of SOX17 is highly heterogenous across multiple cancer types, indicating that SOX17 manifests as a cancer type-dependent feature. Furthermore, the expression pattern of SOX17 is also associated with cancer prognosis in certain cancer types. Strong SOX17 expression correlates with the potency of small molecule drugs that affect PI3K/mTOR signaling. FGF18, a gene highly relevant to SOX17, is involved in the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that SOX17 is mainly expressed in endothelial cells and barely expressed in other cells but spreads to other cell types during the development of ovarian cancer.
Conclusion: Our study revealed the expression pattern of SOX17 in pan-cancer through bulk and single-cell RNA-seq analyses and determined that SOX17 is related to the diagnosis, staging, and prognosis of some tumors. These findings have clinical implications and may help identify mechanistic pathways amenable to pharmacological interventions.
Keywords: PI3K/mTOR; RNA-seq; SOX17; drug response; endometrial cancer; ovarian cancer; pan-cancer.
Copyright © 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased expression of SOX17 is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):8025-34. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3547-3. Epub 2015 May 14. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25971583
-
Epigenetic regulation of Wnt signaling pathway gene SRY-related HMG-box 17 in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2012 Oct;125(19):3526-31. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012. PMID: 23044318
-
Identifying SOX17 as a Sensitive and Specific Marker for Ovarian and Endometrial Carcinomas.Mod Pathol. 2023 Jan;36(1):100038. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2022.100038. Mod Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36788073
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of TMEFF2, SMOC-2, and SOX17 expression in endometrial carcinoma.Exp Mol Pathol. 2021 Oct;122:104670. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104670. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Exp Mol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34339705
-
SOX17 in cellular reprogramming and cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Dec;67(Pt 1):65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.008. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31419525 Review.
Cited by
-
A cutting-edge investigation of the multifaceted role of SOX family genes in cancer pathogenesis through the modulation of various signaling pathways.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jan 4;25(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01517-6. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39753912 Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Multi-Cancer Genome Profiling: Data from a Single Hospital in Japan.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024 Jan-Feb;21(1):79-87. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20431. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38151295 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
