Grp78 is required for intestinal Kras-dependent glycolysis proliferation and adenomagenesis
- PMID: 37643866
- PMCID: PMC10465924
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202301912
Grp78 is required for intestinal Kras-dependent glycolysis proliferation and adenomagenesis
Abstract
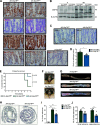
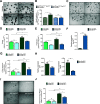
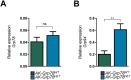
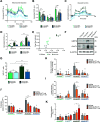
In development of colorectal cancer, mutations in APC are often followed by mutations in oncogene KRAS The latter changes cellular metabolism and is associated with the Warburg phenomenon. Glucose-regulated protein 78 (Grp78) is an important regulator of the protein-folding machinery, involved in processing and localization of transmembrane proteins. We hypothesize that targeting Grp78 in Apc and Kras (AK)-mutant intestines interferes with the metabolic phenotype imposed by Kras mutations. In mice with intestinal epithelial mutations in Apc, Kras G12D and heterozygosity for Grp78 (AK-Grp78 HET ) adenoma number and size is decreased compared with AK-Grp78 WT mice. Organoids from AK-Grp78 WT mice exhibited a glycolysis metabolism which was completely rescued by Grp78 heterozygosity. Expression and correct localization of glucose transporter GLUT1 was diminished in AK-Grp78 HET cells. GLUT1 inhibition restrained the increased growth observed in AK-mutant organoids, whereas AK-Grp78 HET organoids were unaffected. We identify Grp78 as a critical factor in Kras-mutated adenomagenesis. This can be attributed to a critical role for Grp78 in GLUT1 expression and localization, targeting glycolysis and the Warburg effect.
© 2023 Spaan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chang JC, Go S, Gilglioni EH, Duijst S, Panneman DM, Rodenburg RJ, Li HL, Huang HL, Levin LR, Buck J, et al. (2021) Soluble adenylyl cyclase regulates the cytosolic NADH/NAD(+) redox state and the bioenergetic switch between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1862: 148367. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148367 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Colnot S, Niwa-Kawakita M, Hamard G, Godard C, Le Plenier S, Houbron C, Romagnolo B, Berrebi D, Giovannini M, Perret C (2004) Colorectal cancers in a new mouse model of familial adenomatous polyposis: Influence of genetic and environmental modifiers. Lab Invest 84: 1619–1630. 10.1038/labinvest.3700180 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
