Combining nitric oxide and calcium sensing for the detection of endothelial dysfunction
- PMID: 37644120
- PMCID: PMC10465535
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-023-00973-8
Combining nitric oxide and calcium sensing for the detection of endothelial dysfunction
Abstract
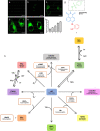
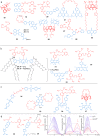
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide and are not typically diagnosed until the disease has manifested. Endothelial dysfunction is an early, reversible precursor in the irreversible development of cardiovascular diseases and is characterized by a decrease in nitric oxide production. We believe that more reliable and reproducible methods are necessary for the detection of endothelial dysfunction. Both nitric oxide and calcium play important roles in the endothelial function. Here we review different types of molecular sensors used in biological settings. Next, we review the current nitric oxide and calcium sensors available. Finally, we review methods for using both sensors for the detection of endothelial dysfunction.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
H.E. and L.J.v.d.B. are employees of Mimetas B.V., which markets the OrganoPlate and holds the registered trademarks OrganoPlate. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- WHO. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases... (2020).
-
- Harvard Health Publishing. Cardiac exercise stress testing: what it can and cannot tell you. https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-disease-overview/cardiac-exercise-s... (2020).
-
- Murad F. Discovery of some of the biological effects of nitric oxide and its role in cell signaling (Nobel Lecture) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999;38:1856–1868. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

