Novel PEGylated cholephytosomes for targeting fisetin to breast cancer: in vitro appraisal and in vivo antitumoral studies
- PMID: 37644299
- PMCID: PMC10761494
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-023-01409-5
Novel PEGylated cholephytosomes for targeting fisetin to breast cancer: in vitro appraisal and in vivo antitumoral studies
Abstract
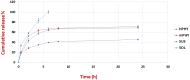
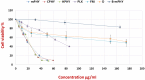
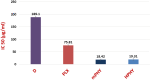
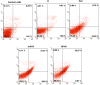
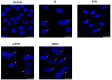
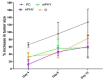
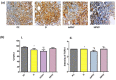
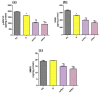
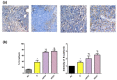
Fisetin (FIS) is a multifunctional bioactive flavanol that has been recently exploited as anticancer drug against various cancers including breast cancer. However, its poor aqueous solubility has constrained its clinical application. In the current work, fisetin is complexed for the first time with soy phosphatidylcholine in the presence of cholesterol to form a novel biocompatible phytosomal system entitled "cholephytosomes." To improve fisetin antitumor activity against breast cancer, stearylamine bearing cationic cholephytosomes (mPHY) were prepared and furtherly modified with hyaluronic acid (HPHY) to allow their orientation to cancer cells through their surface exposed phosphatidylserine and CD-44 receptors, respectively. In vitro characterization studies revealed promising physicochemical properties of both modified vesicles (mPHY and HPHY) including excellent FIS complexation efficiency (˷100%), improved octanol/water solubility along with a sustained drug release over 24 h. In vitro cell line studies against MDA-MB-231 cell line showed about 10- and 3.5-fold inhibition in IC50 of modified vesicles compared with free drug and conventional drug-phospholipid complex, respectively. Preclinical studies revealed that both modified cholephytosomes (mPHY and HPHY) had comparable cytotoxicity that is significantly surpassing free drug cytotoxicity. TGF-β1and its non-canonical related signaling pathway; ERK1/2, NF-κB, and MMP-9 were involved in halting tumorigenesis. Thus, tailoring novel phytosomal nanosystems for FIS could open opportunity for its clinical utility against cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cholephytosomes; Fisetin; Hyaluronic; Stearylamine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Self-assembled fisetin-phospholipid complex: Fisetin-integrated phytosomes for effective delivery to breast cancer.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023 Aug;189:174-188. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.06.009. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023. PMID: 37343893
-
Bioflavonoid Fisetin Loaded α-Tocopherol-Poly(lactic acid)-Based Polymeric Micelles for Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy in Breast Cancers.Pharm Res. 2017 Feb;34(2):453-461. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-2077-z. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28004315
-
Preparation and optimization of poly (lactic acid) nanoparticles loaded with fisetin to improve anti-cancer therapy.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Mar 15;125:700-710. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30521927
-
Role of Fisetin in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 5;15(21):4686. doi: 10.3390/nu15214686. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological effects and mechanisms of fisetin in cancer: a promising anti-cancer agent.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Aug 25;28(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01271-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37626424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fisetin as a chemoprotective and chemotherapeutic agent: mechanistic insights and future directions in cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 12;42(4):104. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02664-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40074915 Review.
-
Harnessing Polyphenols and Novel Delivery Strategies for Effective Treatment of Breast Cancer.Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2025;19(2):127-141. doi: 10.2174/0126673878329992250112190329. Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2025. PMID: 39865821 Review.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Nanoliposomes as Delivery Systems for Fisetin: Stability, Membrane Fluidity, and Bioavailability.Foods. 2024 Jul 29;13(15):2406. doi: 10.3390/foods13152406. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123596 Free PMC article.
-
Newly synthesized chitosan nanoparticles loaded with caffeine/moringa leaf extracts Halt Her2, BRCA1, and BRCA2 expressions.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67599-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103402 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative approaches in breast cancer therapy: repurposing nanocarriers for enhanced outcomes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 1. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04012-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40167629 Review.
References
-
- Harbeck N, et al. “Breast cancer". Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5(1). 10.1038/s41572-019-0111-2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

