Repeat length of C9orf72-associated glycine-alanine polypeptides affects their toxicity
- PMID: 37644512
- PMCID: PMC10463776
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-023-01634-6
Repeat length of C9orf72-associated glycine-alanine polypeptides affects their toxicity
Abstract
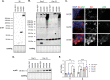
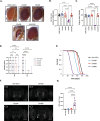
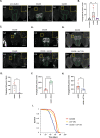
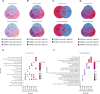
G4C2 hexanucleotide repeat expansions in a non-coding region of the C9orf72 gene are the most common cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). G4C2 insertion length is variable, and patients can carry up to several thousand repeats. Dipeptide repeat proteins (DPRs) translated from G4C2 transcripts are thought to be a main driver of toxicity. Experiments in model organisms with relatively short DPRs have shown that arginine-rich DPRs are most toxic, while polyGlycine-Alanine (GA) DPRs cause only mild toxicity. However, GA is the most abundant DPR in patient brains, and experimental work in animals has generally relied on the use of low numbers of repeats, with DPRs often tagged for in vivo tracking. Whether repeat length or tagging affect the toxicity of GA has not been systematically assessed. Therefore, we generated Drosophila fly lines expressing GA100, GA200 or GA400 specifically in adult neurons. Consistent with previous studies, expression of GA100 and GA200 caused only mild toxicity. In contrast, neuronal expression of GA400 drastically reduced climbing ability and survival of flies, indicating that long GA DPRs can be highly toxic in vivo. This toxicity could be abolished by tagging GA400. Proteomics analysis of fly brains showed a repeat-length-dependent modulation of the brain proteome, with GA400 causing earlier and stronger changes than shorter GA proteins. PolyGA expression up-regulated proteins involved in ER to Golgi trafficking, and down-regulated proteins involved in insulin signalling. Experimental down-regulation of Tango1, a highly conserved regulator of ER-to Golgi transport, partially rescued GA400 toxicity, suggesting that misregulation of this process contributes to polyGA toxicity. Experimentally increasing insulin signaling also rescued GA toxicity. In summary, our data show that long polyGA proteins can be highly toxic in vivo, and that they may therefore contribute to ALS/FTD pathogenesis in patients.
Keywords: C9orf72; Drosophila; Glycine–alanine; Repeat length; Toxicity.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycine-alanine dipeptide repeats spread rapidly in a repeat length- and age-dependent manner in the fly brain.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Dec 16;7(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0860-x. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31843021 Free PMC article.
-
Senataxin helicase, the causal gene defect in ALS4, is a significant modifier of C9orf72 ALS G4C2 and arginine-containing dipeptide repeat toxicity.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Oct 17;11(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01665-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37845749 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of C9orf72-associated dipeptide repeat peptides is modified by commonly used protein tags.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Jun 12;6(9):e202201739. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201739. Print 2023 Sep. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37308278 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine-rich dipeptide-repeat proteins as phase disruptors in C9-ALS/FTD.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020 Dec 11;4(3):293-305. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20190167. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32639008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C9orf72 ALS-FTD: recent evidence for dysregulation of the autophagy-lysosome pathway at multiple levels.Autophagy. 2021 Nov;17(11):3306-3322. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1872189. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33632058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Dipeptide Repeat Proteins on FUS/TDP43-RNA Condensation in C9orf72 ALS/FTD.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Oct 3;128(39):9405-9417. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c04663. Epub 2024 Sep 23. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39311028 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding Nucleotide Repeat Expansion Diseases: Novel Insights from Drosophila melanogaster Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 2;25(21):11794. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111794. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Evidence of Golgi Stress Signaling for Neuropathies.Neurol Int. 2024 Mar 7;16(2):334-348. doi: 10.3390/neurolint16020024. Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38525704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, et al. Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in non-coding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron. 2011;72:245–256. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

