Biotechnologies for bulk production of microalgal biomass: from mass cultivation to dried biomass acquisition
- PMID: 37644516
- PMCID: PMC10466707
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-023-02382-4
Biotechnologies for bulk production of microalgal biomass: from mass cultivation to dried biomass acquisition
Abstract
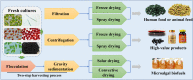
Microalgal biomass represents a sustainable bioresource for various applications, such as food, nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, feed, and other bio-based products. For decades, its mass production has attracted widespread attention and interest. The process of microalgal biomass production involves several techniques, mainly cultivation, harvesting, drying, and pollution control. These techniques are often designed and optimized to meet optimal growth conditions for microalgae and to produce high-quality biomass at acceptable cost. Importantly, mass production techniques are important for producing a commercial product in sufficient amounts. However, it should not be overlooked that microalgal biotechnology still faces challenges, in particular the high cost of production, the lack of knowledge about biological contaminants and the challenge of loss of active ingredients during biomass production. These issues involve the research and development of low-cost, standardized, industrial-scale production equipment and the optimization of production processes, as well as the urgent need to increase the research on biological contaminants and microalgal active ingredients. This review systematically examines the global development of microalgal biotechnology for biomass production, with emphasis on the techniques of cultivation, harvesting, drying and control of biological contaminants, and discusses the challenges and strategies to further improve quality and reduce costs. Moreover, the current status of biomass production of some biotechnologically important species has been summarized, and the importance of improving microalgae-related standards for their commercial applications is noted.
Keywords: Biological contaminant control; Biomass; Cultivation; Drying; Harvesting; Microalgal biotechnology.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Masojídek J, Torzillo G. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014. Mass cultivation of freshwater microalgae.
-
- Hur SB, Bae JH, Youn J-Y, Jo MJ. KMMCC-Korea marine microalgae culture center: list of strains, 2nd edition. Algae. 2015;30:S1–S188.
-
- Ponnuswamy I, Madhavan S, Shabudeen S. Isolation and characterization of green microalgae for carbon sequestration, waste water treatment and bio-fuel production. Int J Bio-Sci Bio-Technol. 2013;5(2):17–26.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
