Transition of patients with metabolic bone disease from paediatric to adult healthcare services: current situation and proposals for improvement
- PMID: 37644568
- PMCID: PMC10463506
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-023-02856-6
Transition of patients with metabolic bone disease from paediatric to adult healthcare services: current situation and proposals for improvement
Abstract
Background: There are currently no models for the transition of patients with metabolic bone diseases (MBDs) from paediatric to adult care. The aim of this project was to analyse information on the experience of physicians in the transition of these patients in Spain, and to draw up consensus recommendations with the specialists involved in their treatment and follow-up.
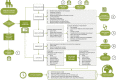
Methods: The project was carried out by a group of experts in MBDs and included a systematic review of the literature for the identification of critical points in the transition process. This was used to develop a questionnaire with a total of 48 questions that would determine the degree of consensus on: (a) the rationale for a transition programme and the optimal time for the patient to start the transition process; (b) transition models and plans; (c) the information that should be specified in the transition plan; and (d) the documentation to be created and the training required. Recommendations and a practical algorithm were developed using the findings. The project was endorsed by eight scientific societies.
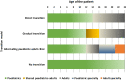
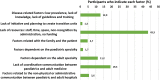
Results: A total of 86 physicians from 53 Spanish hospitals participated. Consensus was reached on 45 of the 48 statements. There was no agreement that the age of 12 years was an appropriate and feasible point at which to initiate the transition in patients with MBD, nor that a gradual transition model could reasonably be implemented in their own hospital. According to the participants, the main barriers for successful transition in Spain today are lack of resources and lack of coordination between paediatric and adult units.
Conclusions: The TEAM Project gives an overview of the transition of paediatric MBD patients to adult care in Spain and provides practical recommendations for its implementation.
Keywords: Metabolic bone disease; Paediatric; Transitional care; X-linked hypophosphataemia (XLH).
© 2023. Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM).
Conflict of interest statement
Yoko Olmedilla is an employee of Kyowa Kirin Farmaceutica, S.L. Begoña Soler was engaged to carry out the design, monitoring, statistical analysis and management of any publications derived from the study. Guillem Pintos received fees from Kyowa Kirin Farmacéutica, S.L. for coordination of the study, for consulting and as a speaker. José Jesús Broseta received fees for presentations and consulting from Kyowa Kirin. The other authors received fees from Kyowa Kirin Farmaceutica, S.L. for coordination of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Kipps S, Bahu T, Ong K, Ackland FM, Brown RS, Fox CT, et al. Current methods of transfer of young people with Type 1 diabetes to adult services. Diabet Med. 2002;19(8):649–654. - PubMed
-
- McDonagh JE, Southwood TR, Shaw KL. Unmet education and training needs of rheumatology health professionals in adolescent health and transitional care. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Reid GJ, Irvine MJ, McCrindle BW, Sananes R, Ritvo PG, Siu SC, et al. Prevalence and correlates of successful transfer from pediatric to adult health care among a cohort of young adults with complex congenital heart defects. Pediatrics. 2004;113:e197–205. - PubMed
-
- Watson AR. Problems and pitfalls of transition from paediatric to adult renal care. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20(2):113–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

