Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promoting knee joint chondrogenesis for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review
- PMID: 37644595
- PMCID: PMC10466768
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-04131-7
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promoting knee joint chondrogenesis for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: The onset of OA is affected by a variety of factors, which eventually lead to the loss of cartilage in the joints, the formation of osteophytes, the loss of normal knee mobility, and pain and discomfort, which seriously affects the quality of life. HUC-MSCs can promote cartilage production and have been widely used in research in the past decade. This article systematically summarizes that it is well used in basic research and clinical studies to promote inflammatory chondrogenesis in the treatment of OA. Provide a theoretical basis for clinical treatment.
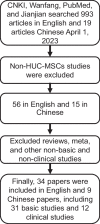
Patients and methods: This study collected CNKI, Wanfang, PubMed, and articles related to the treatment of OA with HUC-MSCs since their publication, excluding non-basic and clinical studies such as reviews and meta-analysis. A total of 31 basic experimental studies and 12 clinical studies were included. Systematically analyze the effects of HUC-MSCs on inhibiting inflammatory factors, promoting chondrocyte production, and current clinical treatment.
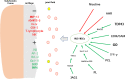
Results: HUC-MSCs can reduce inflammatory factors such as MMP-13, ADAMTS-5, IL-1β, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, induced conversion from M1 to M2 in OA to protect cartilage damage and reduce OA inflammation. Synthesize ColII, SOX9, and aggrecan at the same time to promote cartilage synthesis.
Conclusion: HUC-MSCs not only have typical stem cell biological characteristics, but also have rich sources and convenient material extraction. Compared with stem cells from other sources, HUC-MSCs have stronger proliferation, differentiation, and immune regulation abilities. Furthermore, there are no ethical issues associated with their use.
Safety: Primarily attributed to pain, the majority of individuals experience recovery within 24 h following injection. HUC-MSCs possess the ability to alleviate pain, enhance knee joint function, and potentially postpone the need for surgical intervention in both non-surgical and other cases, making them highly deserving of clinical promotion and application.
Keywords: Chondrocytes; Exosomes; Inflammation; Knee; Osteoarthritis; Regenerative medicine; Safety.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Samara O, Jafar H, Hamdan M, et al. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection of expanded umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis: a safety/efficacy study with MRI data. Regen Med. 2022;17(5):299–312. - PubMed
-
- Shi D, Clement ND, Bhonde R, Ikegawa S, Mascarenhas VV, Di Matteo B, Indelli PF, Kourkoumelis N, Rodríguez-Merchán EC, Sheykhhasan M, Fu FH, Vaz MA, Kong J, Azantsa BG, Ye C, Halabchi F, Cornish SM, Hausmann LR, Campos ALS, Lopes de Jesus CC, Jorgensen C, Ilieva EM, Wang W, Villarreal-Martínez L, Ahn H, Shirinsky IV, Cheung C, Knutsen G, Petersen W, Lane NE, Cai H, Xu W, Wu J, Zhang Y, Lu J, Jiang Q. Society for translational medicine-expert consensus on the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann Joint. 2019;4:49. doi: 10.21037/aoj.2019.12.13. - DOI
-
- Xing D, Wu J, Wang B, et al. Intra-articular delivery of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells temporarily retard the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020;23(6):778–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous