Analysis of genetic factors associated with fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37644826
- PMCID: PMC10524060
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.6410
Analysis of genetic factors associated with fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in PNPLA3 and hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13 (HSD17B13) genes are associated with fatty liver disease (FLD) progression and carcinogenesis. In the present study, we evaluated the characteristics of Japanese FLD patients according to HSD17B13 polymorphisms.
Methods: We enrolled 402 patients who were clinically and pathologically diagnosed with FLD (alcoholic: 63 cases, nonalcoholic: 339 cases) at our hospital in 1990-2018 (228 males; median age: 54.9 [14.6-83.6] years). FLD patients with HSD17B13 A/A (212 cases) and others (A/AA or AA/AA; 190 cases) were compared.
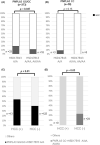
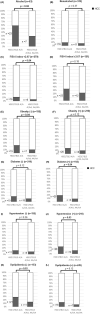
Results: Compared to patients with HSD17B13 A/A and others, those with the A/A genotype showed increased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (A/A vs. others; 18.4% vs. 9.5%, p = 0.01), cardiovascular diseases (14.2% vs. 4.2%, p < 0.01), and hypertension (56.6% vs. 47.4%, p = 0.06). In patients without A/A, the HCC incidence was significantly reduced in those with alcohol-related FLD, fibrosis-4 index <2.67, and the PNPLA3 CC genotype; however, there was no significant difference in nonalcoholic-FLD. Patients without HSD17B13 A/A showed severe steatosis (77% vs. 88.6%, p < 0.01). New HCC developed in 11 cases and the 5-year incidence rate of HCC was 3.3% in patients with both PNPLA3 GG/GC and HSD17B13 A/A, which was significantly higher than the rate for those with other SNP profiles (0.6%, p = 0.03).
Conclusions: Inhibiting HSD17B13 activity may prevent HCC development, particularly in alcohol-related FLD and low-risk patients. Therefore, combinations of SNPs and other risk factors can be used for screening FLD-HCC.
Keywords: 17-beta dehydrogenase 13; fatty liver disease; hepatocellular carcinoma; patatin-like phospholipase 3.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
KT is the recipient of research funding from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AbbVie GK, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Asahi Kasei Corporation. Ajinomoto Co., Inc., and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Eslam M, Valenti L, Romeo S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: clinical impact. J Hepatol. 2018;68:268‐279. - PubMed
-
- Liu YL, Patman GL, Leathart JB, et al. Carriage of the PNPLA3 rs738409 C >G polymorphism confers an increased risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2014;61:75‐81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

