Genome-wide association study reveals genomic loci of sex differentiation and gonadal development in Plectropomus leopardus
- PMID: 37645057
- PMCID: PMC10461086
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1229242
Genome-wide association study reveals genomic loci of sex differentiation and gonadal development in Plectropomus leopardus
Abstract
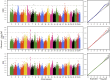
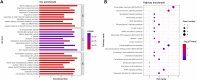
Introduction: Plectropomus leopardus, a commercially significant marine fish, is primarily found in the Western Pacific regions and along the coast of Southeast Asia. A thorough analysis of the molecular mechanisms involved in sex differentiation is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of gonadal development and improving sex control breeding. However, the relevant fundamental studies of P. leopardus are relatively lacking. Methods: In this study, a genome-wide association study (GWAS) was conducted to investigate the genetic basis mechanism of sex differentiation and gonadal developmental traits in P. leopardus utilizing about 6,850,000 high-quality single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) derived from 168 individuals (including 126 females and 42 males) by the genome-wide efficient mixed-model association (GEMMA) algorithm. Results: The results of these single-trait GWASs showed that 46 SNP loci (-log10 p > 7) significantly associated with sex differentiation, and gonadal development traits were distributed in multiple different chromosomes, which suggested the analyzed traits were all complex traits under multi-locus control. A total of 1,838 potential candidate genes were obtained by considering a less-stringent threshold (-log10 p > 6) and ±100 kb regions surrounding the significant genomic loci. Moreover, 31 candidate genes were identified through a comprehensive analysis of significant GWAS peaks, gene ontology (GO) annotations, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses, including taf7, ddx6, apoeb, sgk1, a2m, usf1, hsd3b7, dll4, xbp1, tet3, esr1, and gli3. These trait-associated genes have been shown to be involved in germline development, male sex differentiation, gonad morphogenesis, hormone receptor binding, oocyte development, male gonad development, steroidogenesis, estrogen-synthetic pathway, etc. Discussion: In the present study, multiple genomic loci of P. leopardus associated with sex differentiation and gonadal development traits were identified for the first time by using GWAS, providing a valuable resource for further research on the molecular genetic mechanism and sex control in P. leopardus. Our results also can contribute to understanding the genetic basis of the sex differentiation mechanism and gonadal development process in grouper fish.
Keywords: Plectropomus leopardus; candidate genes; genome-wide association study; genomic loci; gonadal development; sex differentiation.
Copyright © 2023 Gao, Wang, Liu, Chen, Guo, Ke, Wang, Luo and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deciphering the population structure and genetic basis of growth traits from whole-genome resequencing of the leopard coral grouper ( Plectropomus leopardus).Zool Res. 2024 Mar 18;45(2):329-340. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.270. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38485503 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis of black color trait in the leopard coral grouper (Plectropomus leopardus) using whole genome resequencing.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2023 Dec;48:101138. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2023.101138. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37683359
-
Theoretical Analysis and Expression Profiling of 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Genes in Gonadal Development and Steroidogenesis of Leopard Coral Grouper (Plectropomus leopardus).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 11;25(4):2180. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042180. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396857 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of candidate gene networks involved in resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean.J Appl Genet. 2022 Feb;63(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s13353-021-00654-z. Epub 2021 Sep 11. J Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 34510383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring associations between estrogen and gene candidates identified by coronary artery disease genome-wide association studies.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Mar 20;12:1502985. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1502985. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40182431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Resequencing Analyses Revealed Genetic Diversity and Selection Signatures during Rabbit Breeding and Improvement.Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 29;15(4):433. doi: 10.3390/genes15040433. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674368 Free PMC article.
-
Combining ATAC-seq and RNA-seq reveals key genes for gonadal abnormalities in one-month-old XX-DSD pigs.BMC Genomics. 2025 May 6;26(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11613-x. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40329180 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a candidate sex determination region and sex-specific molecular markers based on whole-genome re‑sequencing in the sea star Asterias amurensis.DNA Res. 2024 Dec 27;32(1):dsaf003. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsaf003. DNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39792457 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study for Weight-Related Traits in Scylla paramamosain Using Whole-Genome Resequencing.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jun 20;15(13):1829. doi: 10.3390/ani15131829. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40646730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams S., Mapstone B. D., Russ G. R., Davies C. R. (2000). Geographic variation in the sex ratio, sex specific size, and age structure of Plectropomus leopardus (Serranidae) between reefs open and closed to fishing on the Great Barrier Reef. Can. J. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 57, 1448–1458. 10.1139/f00-076 - DOI
-
- Adams S. (2003). Morphological ontogeny of the gonad of three plectropomid species through sex differentiation and transition. J. Fish. Biol. 63, 22–36. 10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00098.x - DOI
-
- Adolfi M. C., Carreira A. C., Jesus L. W., Bogerd J., Funes R. M., Schartl M., et al. (2015). Molecular cloning and expression analysis of dmrt1 and sox9 during gonad development and male reproductive cycle in the lambari fish, Astyanax altiparanae . Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 13, 2. 10.1186/1477-7827-13-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

