Novel receptor, mutation, vaccine, and establishment of coping mode for SARS-CoV-2: current status and future
- PMID: 37645223
- PMCID: PMC10461067
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1232453
Novel receptor, mutation, vaccine, and establishment of coping mode for SARS-CoV-2: current status and future
Abstract
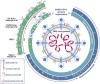
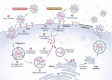
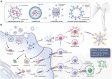
Since the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its resultant pneumonia in December 2019, the cumulative number of infected people worldwide has exceeded 670 million, with over 6.8 million deaths. Despite the marketing of multiple series of vaccines and the implementation of strict prevention and control measures in many countries, the spread and prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 have not been completely and effectively controlled. The latest research shows that in addition to angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2), dozens of protein molecules, including AXL, can act as host receptors for SARS-CoV-2 infecting human cells, and virus mutation and immune evasion never seem to stop. To sum up, this review summarizes and organizes the latest relevant literature, comprehensively reviews the genome characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 as well as receptor-based pathogenesis (including ACE2 and other new receptors), mutation and immune evasion, vaccine development and other aspects, and proposes a series of prevention and treatment opinions. It is expected to provide a theoretical basis for an in-depth understanding of the pathogenic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 along with a research basis and new ideas for the diagnosis and classification, of COVID-19-related disease and for drug and vaccine research and development.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccines; Omicron variant; attachment factors; entry receptors; heterologous booster immunization; small molecule antiviral drugs.
Copyright © 2023 Zeng, Geng, Wen, Chen, Zhu, Dong, Hao, Wang, Yang, Zhang, Zheng, Sun and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
A mosaic-type trimeric RBD-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate induces potent neutralization against Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants.Elife. 2022 Aug 25;11:e78633. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78633. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36004719 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Immune Evasion and Host Range Expansion by the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0041623. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00416-23. Epub 2023 Apr 3. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37010428 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2-Independent Alternative Receptors for SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2022 Nov 16;14(11):2535. doi: 10.3390/v14112535. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36423144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles of natural product-derived medicines: Beyond the pandemic.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 19;11(4):e42739. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42739. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40083991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimating the prevalence of persistent symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection (post-COVID-19 syndrome): a regional cross-sectional study protocol.BMJ Open. 2025 May 30;15(5):e093844. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093844. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40447416 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Alternative Receptors for SARS-CoV-2-Induced Kidney Damage: TLR-4, KIM-1/TIM-1, and CD147.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Jan 12;29(1):8. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2901008. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38287815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

