Hepatitis B virus serum RNA transcript isoform composition and proportion in chronic hepatitis B patients by nanopore long-read sequencing
- PMID: 37645229
- PMCID: PMC10461054
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1233178
Hepatitis B virus serum RNA transcript isoform composition and proportion in chronic hepatitis B patients by nanopore long-read sequencing
Abstract
Introduction: Serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) RNA is a promising new biomarker to manage and predict clinical outcomes of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection. However, the HBV serum transcriptome within encapsidated particles, which is the biomarker analyte measured in serum, remains poorly characterized. This study aimed to evaluate serum HBV RNA transcript composition and proportionality by PCR-cDNA nanopore sequencing of samples from CHB patients having varied HBV genotype (gt, A to F) and HBeAg status.
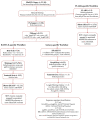
Methods: Longitudinal specimens from 3 individuals during and following pregnancy (approximately 7 months between time points) were also investigated. HBV RNA extracted from 16 serum samples obtained from 13 patients (73.3% female, 84.6% Asian) was sequenced and serum HBV RNA isoform detection and quantification were performed using three bioinformatic workflows; FLAIR, RATTLE, and a GraphMap-based workflow within the Galaxy application. A spike-in RNA variant (SIRV) control mix was used to assess run quality and coverage. The proportionality of transcript isoforms was based on total HBV reads determined by each workflow.
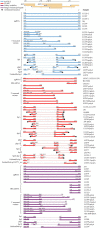
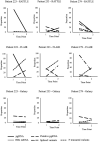
Results: All chosen isoform detection workflows showed high agreement in transcript proportionality and composition for most samples. HBV pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) was the most frequently observed transcript isoform (93.8% of patient samples), while other detected transcripts included pgRNA spliced variants, 3' truncated variants and HBx mRNA, depending on the isoform detection method. Spliced variants of pgRNA were primarily observed in HBV gtB, C, E, or F-infected patients, with the Sp1 spliced variant detected most frequently. Twelve other pgRNA spliced variant transcripts were identified, including 3 previously unidentified transcripts, although spliced isoform identification was very dependent on the workflow used to analyze sequence data. Longitudinal sampling among pregnant and post-partum antiviral-treated individuals showed increasing proportions of 3' truncated pgRNA variants over time.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated long-read sequencing as a promising tool for the characterization of the serum HBV transcriptome. However, further studies are needed to better understand how serum HBV RNA isoform type and proportion are linked to CHB disease progression and antiviral treatment response.
Keywords: hepatitis B virus; long-read sequencing; nanopore; pgRNA; serum HBV RNA; spliced RNA; transcript.
Copyright © 2023 Vachon, Seo, Patel, Coffin, Marinier, Eyras and Osiowy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum hepatitis B virus RNA detectability, composition and clinical significance in patients with ab initio hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B.Virol J. 2022 Jan 29;19(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01749-7. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35093105 Free PMC article.
-
A standardized assay for the quantitative detection of serum HBV RNA in chronic hepatitis B patients.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):775-785. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2045874. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35220917 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted long-read sequencing reveals clonally expanded HBV-associated chromosomal translocations in patients with chronic hepatitis B.JHEP Rep. 2022 Feb 12;4(4):100449. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100449. eCollection 2022 Apr. JHEP Rep. 2022. PMID: 35295767 Free PMC article.
-
Progression and status of antiviral monitoring in patients with chronic hepatitis B: From HBsAg to HBV RNA.World J Hepatol. 2018 Sep 27;10(9):603-611. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i9.603. World J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30310538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: case selection and duration of therapy.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Apr;17(4):409-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02767.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 11982721 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription.Viruses. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):609. doi: 10.3390/v16040609. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Management of Chronic Hepatitis B: 2025 Guidelines Update from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver and Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada.Can Liver J. 2025 May 26;8(2):368-440. doi: 10.3138/canlivj-2025-0012-e. eCollection 2025 May. Can Liver J. 2025. PMID: 40677987 Free PMC article.
-
SMC5/6-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation of Hepatitis B Virus and Its Therapeutic Potential.Viruses. 2024 Oct 25;16(11):1667. doi: 10.3390/v16111667. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asadi-Asadabad S., Sarvnaz H., Amiri M. M., Mobini M., Khoshnoodi J., Hojjat-Farsangi M., et al. . (2021). Influence of pattern recognition receptor ligands on induction of innate immunity and control of hepatitis B virus infection. Viral Immunol. 34, 531–541. doi: 10.1089/vim.2021.0040 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

