Melatonin as a regulator of apoptosis in leukaemia: molecular mechanism and therapeutic perspectives
- PMID: 37645444
- PMCID: PMC10461318
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1224151
Melatonin as a regulator of apoptosis in leukaemia: molecular mechanism and therapeutic perspectives
Abstract
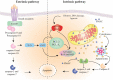
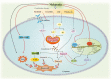
Leukaemia is a dangerous malignancy that causes thousands of deaths every year throughout the world. The rate of morbidity and mortality is significant despite many advancements in therapy strategies for affected individuals. Most antitumour medications used now in clinical oncology use apoptotic signalling pathways to induce cancer cell death. Accumulated data have shown a direct correlation between inducing apoptosis in cancer cells with higher tumour regression and survival. Until now, the efficacy of melatonin as a powerful antitumour agent has been firmly established. A change in melatonin concentrations has been reported in multiple tumours such as endometrial, hematopoietic, and breast cancers. Findings show that melatonin's anticancer properties, such as its prooxidation function and ability to promote apoptosis, indicate the possibility of utilizing this natural substance as a promising agent in innovative cancer therapy approaches. Melatonin stimulates cell apoptosis via the regulation of many apoptosis facilitators, including mitochondria, cytochrome c, Bcl-2, production of reactive oxygen species, and apoptosis receptors. This paper aimed to further assess the anticancer effects of melatonin through the apoptotic pathway, considering the role that cellular apoptosis plays in the pathogenesis of cancer. The effect of melatonin may mean that it is appropriate for use as an adjuvant, along with other therapeutic approaches such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Keywords: apoptosis; leukaemia; melatonin; signalling pathway; therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Mafi, Rismanchi, Gholinezhad, Mohammadi, Mousavi, Hosseini, Milasi, Reiter, Ghezelbash, Rezaee, Sheida, Zarepour, Asemi, Mansournia and Mirzaei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Afacan Ozturk H. B., Albayrak M., Maral S., Reis Aras M., Yilmaz F., Akyol P., et al. (2021). Hypercalcemia associated with the interaction between all trans retinoic acid and posaconazole in an acute promyelocytic leukemia case. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 27 (8), 2027–2029. 10.1177/10781552211007889 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alonso-González C., González A., Martínez-Campa C., Menéndez-Menéndez J., Gómez-Arozamena J., García-Vidal A., et al. (2016). Melatonin enhancement of the radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells is associated with the modulation of proteins involved in estrogen biosynthesis. Cancer Lett. 370 (1), 145–152. 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.015 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

