The Optimization of Medium Conditions and Auxins in the Induction of Adventitious Roots of Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L.) and Their Phytochemical Constituents
- PMID: 37645570
- PMCID: PMC10462441
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/2983812
The Optimization of Medium Conditions and Auxins in the Induction of Adventitious Roots of Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L.) and Their Phytochemical Constituents
Abstract
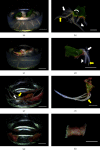
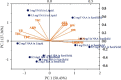
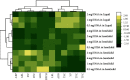
Pokeweed, Phytolacca americana L., is considered a widely spreading invasive plant, while saponin contents accumulated in the roots have pharmaceutical uses, such as rheumatism treatments and anti-inflammation. Adventitious root cultures are an important source of diverse secondary metabolites, which have significant applications in various fields. This study focused on the optimization of parameters for root induction using different medium states and treatments with auxins on a pokeweed leaf. Semisolid and liquid MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) media were supplemented with indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) and 1-naphthylacetic acid (NAA) at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mg/L. Root growth parameters, e.g., induction percentage, root numbers, length, and weight, were measured to determine the adventitious root induction efficiency. Total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, total saponin content, and antioxidant activity were recorded. Results showed that adventitious roots induced in semisolid MS medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/L NAA exhibited a high density of lateral roots. Appropriate medium state and auxin for adventitious root induction in pokeweed were determined as semisolid medium supplemented with 2 mg/L NAA. Considering phytochemicals, adventitious roots induced in liquid medium containing 0.5-1 mg/L NAA had the highest yield extract percentage. Additionally, adventitious roots cultivated in a liquid medium enriched with 1 mg/L NAA exhibited the highest phenolic and saponin contents. A principal component analysis (PCA) biplot and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) heatmap demonstrated different response patterns between semisolid and liquid media applied with NAA. The results of the semisolid media were grouped together due to high expression levels of the root induction parameters, while elevated phytochemical values were observed in the liquid media treatments. The results suggested two different media that provide the highest adventitious root induction efficiency and the greatest phytochemical contents: semisolid medium with 2 mg/L NAA and liquid medium with 1 mg/L NAA, respectively. These culture media can be applied to optimize adventitious root culture of pokeweed and in vitro phytochemical production.
Copyright © 2023 Attachai Trunjaruen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micropropagation of pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L.) and comparison of phenolic, flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity between pokeweed callus and other parts.PeerJ. 2022 Feb 7;10:e12892. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12892. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35186483 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro production of atractylon and β-eudesmol from Atractylodes chinensis by adventitious root culture.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Nov;106(21):7027-7037. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12194-5. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36171502
-
Optimization of adventitious root culture for production of biomass and secondary metabolites in Prunella vulgaris L.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Nov;174(6):2086-95. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-1190-x. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25163888
-
Production of biomass and bioactive compounds from adventitious roots by optimization of culturing conditions of Eurycoma longifolia in balloon-type bubble bioreactor system.J Biosci Bioeng. 2015 Jun;119(6):712-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.11.010. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015. PMID: 25511788
-
Optimization of High-Efficiency Tissue Culture Regeneration Systems in Gray Poplar.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 11;13(9):1896. doi: 10.3390/life13091896. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balogh L., Juhasz M. American and Chinese pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L., Ph. esculenta van Houtte) In: Botta-Dukat Z., Balogh L., editors. The Most Invasive Plants in Hungary . Hungary: HAS Institute of Ecology and Botany; 2008. pp. 35–46.
-
- Hodgson E. Toxins and venoms. In: Hodgeson E., editor. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science . Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Inc; 2012. pp. 373–415. - PubMed
-
- De Smet P. A. G. M. Phytolacca americana. In: De Smet P. A. G. M., editor. Adverse Effects of Herbal Drugs 2 . Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1993. pp. 253–262.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

