A review of low-cost and portable optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 37645660
- PMCID: PMC10465117
- DOI: 10.1088/2516-1091/abfeb7
A review of low-cost and portable optical coherence tomography
Abstract
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a powerful optical imaging technique capable of visualizing the internal structure of biological tissues at near cellular resolution. For years, OCT has been regarded as the standard of care in ophthalmology, acting as an invaluable tool for the assessment of retinal pathology. However, the costly nature of most current commercial OCT systems has limited its general accessibility, especially in low-resource environments. It is therefore timely to review the development of low-cost OCT systems as a route for applying this technology to population-scale disease screening. Low-cost, portable and easy to use OCT systems will be essential to facilitate widespread use at point of care settings while ensuring that they offer the necessary imaging performances needed for clinical detection of retinal pathology. The development of low-cost OCT also offers the potential to enable application in fields outside ophthalmology by lowering the barrier to entry. In this paper, we review the current development and applications of low-cost, portable and handheld OCT in both translational and research settings. Design and cost-reduction techniques are described for general low-cost OCT systems, including considerations regarding spectrometer-based detection, scanning optics, system control, signal processing, and the role of 3D printing technology. Lastly, a review of clinical applications enabled by low-cost OCT is presented, along with a detailed discussion of current limitations and outlook.
Keywords: low cost; ophthalmology; optical coherence tomography; portable imaging modality.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Adam Wax is founder and president of Lumedica, Inc. and Lumedica Vision.
Figures
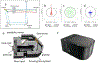

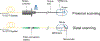

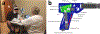



References
-
- Leitgeb R, Hitzenberger C and Fercher AF 2003. Performance of Fourier domain vs. time domain optical coherence tomography Opt. Express 11 889–94 - PubMed
-
- Choma MA, Sarunic MV, Yang C and Izatt JA 2003. Sensitivity advantage of swept source and Fourier domain optical coherence tomography Opt. Express 11 2183–9 - PubMed
-
- de Boer JF, Cense B, Park BH, Pierce MC, Tearney GJ and Bouma BE 2003. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography Opt. Lett 28 2067–9 - PubMed
-
- Wojtkowski M, Leitgeb R, Kowalczyk A, Bajraszewski T and Fercher AF 2002. In vivo human retinal imaging by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography J. Biomed. Opt 7 457–64 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
