This is a preprint.
Clock-dependent chromatin accessibility rhythms regulate circadian transcription
- PMID: 37645872
- PMCID: PMC10462003
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.15.553315
Clock-dependent chromatin accessibility rhythms regulate circadian transcription
Update in
-
Clock-dependent chromatin accessibility rhythms regulate circadian transcription.PLoS Genet. 2024 May 28;20(5):e1011278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011278. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38805552 Free PMC article.
Abstract
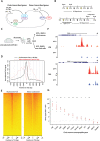
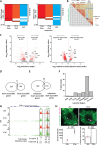
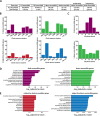
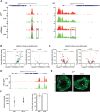
Chromatin organization plays a crucial role in gene regulation by controlling the accessibility of DNA to transcription machinery. While significant progress has been made in understanding the regulatory role of clock proteins in circadian rhythms, how chromatin organization affects circadian rhythms remains poorly understood. Here, we employed ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with Sequencing) on FAC-sorted Drosophila clock neurons to assess genome-wide chromatin accessibility over the circadian cycle. We observed significant circadian oscillations in chromatin accessibility at promoter and enhancer regions of hundreds of genes, with enhanced accessibility either at dusk or dawn, which correlated with their peak transcriptional activity. Notably, genes with enhanced accessibility at dusk were enriched with E-box motifs, while those more accessible at dawn were enriched with VRI/PDP1-box motifs, indicating that they are regulated by the core circadian feedback loops, PER/CLK and VRI/PDP1, respectively. Further, we observed a complete loss of chromatin accessibility rhythms in per01 null mutants, with chromatin consistently accessible throughout the circadian cycle, underscoring the critical role of Period protein in driving chromatin compaction during the repression phase. Together, this study demonstrates the significant role of chromatin organization in circadian regulation, revealing how the interplay between clock proteins and chromatin structure orchestrates the precise timing of biological processes throughout the day. This work further implies that variations in chromatin accessibility might play a central role in the generation of diverse circadian gene expression patterns in clock neurons.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; chromatin accessibility; circadian clock; clock neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have no declared conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
