This is a preprint.
An eQTL-based Approach Reveals Candidate Regulators of LINE-1 RNA Levels in Lymphoblastoid Cells
- PMID: 37645920
- PMCID: PMC10461994
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.15.553416
An eQTL-based Approach Reveals Candidate Regulators of LINE-1 RNA Levels in Lymphoblastoid Cells
Update in
-
An eQTL-based approach reveals candidate regulators of LINE-1 RNA levels in lymphoblastoid cells.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jun 7;20(6):e1011311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011311. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38848448 Free PMC article.
Abstract
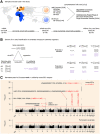
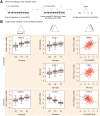
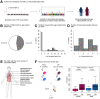
Long interspersed element 1 (L1) are a family of autonomous, actively mobile transposons that occupy ~17% of the human genome. A number of pleiotropic effects induced by L1 (promoting genome instability, inflammation, or cellular senescence) have been observed, and L1's contributions to aging and aging diseases is an area of active research. However, because of the cell type-specific nature of transposon control, the catalogue of L1 regulators remains incomplete. Here, we employ an eQTL approach leveraging transcriptomic and genomic data from the GEUVADIS and 1000Genomes projects to computationally identify new candidate regulators of L1 RNA levels in lymphoblastoid cell lines. To cement the role of candidate genes in L1 regulation, we experimentally modulate the levels of top candidates in vitro, including IL16, STARD5, HSDB17B12, and RNF5, and assess changes in TE family expression by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). Remarkably, we observe subtle but widespread upregulation of TE family expression following IL16 and STARD5 overexpression. Moreover, a short-term 24-hour exposure to recombinant human IL16 was sufficient to transiently induce subtle, but widespread, upregulation of L1 subfamilies. Finally, we find that many L1 expression-associated genetic variants are co-associated with aging traits across genome-wide association study databases. Our results expand the catalogue of genes implicated in L1 RNA control and further suggest that L1-derived RNA contributes to aging processes. Given the ever-increasing availability of paired genomic and transcriptomic data, we anticipate this new approach to be a starting point for more comprehensive computational scans for transposon transcriptional regulators.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An eQTL-based approach reveals candidate regulators of LINE-1 RNA levels in lymphoblastoid cells.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jun 7;20(6):e1011311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011311. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38848448 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals loci linked to human variation in LINE-1- and Alu-insertion numbers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2024.09.10.612283. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.10.612283. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Transl Med Aging. 2025;9:25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tma.2025.02.001. PMID: 39314493 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals loci linked to human variation in LINE-1- and Alu-insertion numbers.Transl Med Aging. 2025;9:25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tma.2025.02.001. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Transl Med Aging. 2025. PMID: 40051556 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsidering LINE-1's role in cancer: does LINE-1 function as a reporter detecting early cancer-associated epigenetic signatures?Evol Med Public Health. 2021 Feb 14;9(1):78-82. doi: 10.1093/emph/eoab004. eCollection 2021. Evol Med Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33717489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long INterspersed element-1 mobility as a sensor of environmental stresses.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020 Apr;61(4):465-493. doi: 10.1002/em.22366. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 32144842 Review.
References
-
- Ahl V, Keller H, Schmidt S, Weichenrieder O. 2015. Retrotransposition and Crystal Structure of an Alu RNP in the Ribosome-Stalling Conformation. Molecular Cell 60: 715–727. - PubMed
-
- Baeken MW, Moosmann B, Hajieva P. 2020. Retrotransposon activation by distressed mitochondria in neurons. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 525: 570–575. - PubMed
-
- Baier M, Werner A, Bannert N, Metzner K, Kurth R. 1995. HIV suppression by interleukin-16. Nature 378: 563. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
