Structural and functional insights into the G protein-coupled receptors: CB1 and CB2
- PMID: 37646476
- PMCID: PMC10586759
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20221316
Structural and functional insights into the G protein-coupled receptors: CB1 and CB2
Abstract
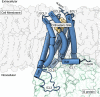
The cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 mediate a variety of physiological processes and continue to be explored as desirable drug targets. Both receptors are activated by the endogenous endocannabinoids and the psychoactive components of marijuana. Over the years, many efforts have been made to make selective ligands; however, the high degree of homology between cannabinoid receptor subtypes introduces challenges in studying either receptor in isolation. Recent advancements in structure biology have resulted in a surge of high-resolution structures, enriching our knowledge and understanding of receptor structure and function. In this review, of recent cannabinoid receptor structures, key features of the inactive and active state CB1 and CB2 are presented. These structures will provide additional insight into the modulation and signaling mechanism of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 and aid in the development of future therapeutics.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptors; cannabinoids; cryo-electron microscopy; crystallography.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Howlett, A.C. (1985) Cannabinoid inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry of the response in neuroblastoma cell membranes. Mol. Pharmacol. 27, 429–436 - PubMed
-
- Devane, W.A., Dysarz, III, F.A., Johnson, M.R., Melvin, L.S. and Howlett, A.C. (1988) Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 34, 605–613 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

