Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to complestatin and corbomycin depends on the VraSR two-component system
- PMID: 37646518
- PMCID: PMC10581084
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00370-23
Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to complestatin and corbomycin depends on the VraSR two-component system
Abstract
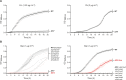
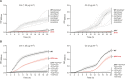
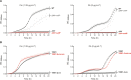
The overuse of antibiotics in humans and livestock has driven the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance and has therefore prompted research on the discovery of novel antibiotics. Complestatin (Cm) and corbomycin (Cb) are glycopeptide antibiotics with an unprecedented mechanism of action that is active even against methicillin-resistant and daptomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. They bind to peptidoglycan and block the activity of peptidoglycan hydrolases required for remodeling the cell wall during growth. Bacterial signaling through two-component transduction systems (TCSs) has been associated with the development of S. aureus antimicrobial resistance. However, the role of TCSs in S. aureus susceptibility to Cm and Cb has not been previously addressed. In this study, we determined that, among all 16 S. aureus TCSs, VraSR is the only one controlling the susceptibility to Cm and Cb. Deletion of vraSR increased bacterial susceptibility to both antibiotics. Epistasis analysis with members of the vraSR regulon revealed that deletion of spdC, which encodes a membrane protein that scaffolds SagB for cleavage of peptidoglycan strands to achieve physiological length, in the vraSR mutant restored Cm and Cb susceptibility to wild-type levels. Moreover, deletion of either spdC or sagB in the wild-type strain increased resistance to both antibiotics. Further analyses revealed a significant rise in the relative amount of peptidoglycan and its total degree of cross-linkage in ΔspdC and ΔsagB mutants compared to the wild-type strain, suggesting that these changes in the cell wall provide resistance to the damaging effect of Cm and Cb. IMPORTANCE Although Staphylococcus aureus is a common colonizer of the skin and digestive tract of humans and many animals, it is also a versatile pathogen responsible for causing a wide variety and number of infections. Treatment of these infections requires the bacteria to be constantly exposed to antibiotic treatment, which facilitates the selection of antibiotic-resistant strains. The development of new antibiotics is, therefore, urgently needed. In this paper, we investigated the role of the sensory system of S. aureus in susceptibility to two new antibiotics: corbomycin and complestatin. The results shed light on the cell-wall synthesis processes that are affected by the presence of the antibiotic and the sensory system responsible for coordinating their activity.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; VraSR; autolysins; complestatin; corbomycin; two-component system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
VraSR two-component regulatory system contributes to mprF-mediated decreased susceptibility to daptomycin in in vivo-selected clinical strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jan;56(1):92-102. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00432-10. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 21986832 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7796):582-587. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1990-9. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32051588
-
VraT/YvqF is required for methicillin resistance and activation of the VraSR regulon in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):83-95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01651-12. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23070169 Free PMC article.
-
The Cell Wall, Cell Membrane and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus aureus and Their Role in Antibiotic Resistance.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 19;11(2):259. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020259. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus cell wall maintenance - the multifaceted roles of peptidoglycan hydrolases in bacterial growth, fitness, and virulence.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022 Oct 28;46(5):fuac025. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuac025. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35675307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Study of desKR: a Lineage-Specific Two-Component System Positively Regulating Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Sep 17;17:4037-4053. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S485049. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. Retraction in: Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 13;17:5579-5580. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S509159. PMID: 39309069 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A mechanistic understanding of the effect of Staphylococcus aureus VraS histidine kinase single-point mutation on antibiotic resistance.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr 15;13(5):e0009525. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00095-25. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40233945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Magiorakos A-P, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, Harbarth S, Hindler JF, Kahlmeter G, Olsson-Liljequist B, Paterson DL, Rice LB, Stelling J, Struelens MJ, Vatopoulos A, Weber JT, Monnet DL. 2012. Multidrug‐resistant, extensively drug‐resistant and pandrug‐resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18:268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

