Pharmacokinetics of Oral Vitamin D in Children with Obesity and Asthma
- PMID: 37646988
- PMCID: PMC10582143
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-023-01285-9
Pharmacokinetics of Oral Vitamin D in Children with Obesity and Asthma
Abstract
Background and objective: Vitamin D insufficiency is common in several pediatric diseases including obesity and asthma. Little data exist describing the pharmacokinetics of oral vitamin D in children or the optimal dosing to achieve therapeutic 25(OH)D targets. Describe the pharmacokinetics of oral Vitamin D in children with asthma.
Methods: This was a multi-center, randomized, open-label, oral supplementation study to describe the pharmacokinetics of vitamin D in children aged 6-17 years who have asthma and were overweight/obese. Participants had a serum 25(OH)D concentration between 10 and < 30 ng/mL at baseline. In Part 1 of the study, we assessed four 16-week dosing regimens for their ability to achieve 25(OH)D concentrations ≥ 40 ng/mL. Using serial serum 25(OH)D sampling over 28 weeks, we created a population pharmacokinetic model and performed dosing simulations to achieve 25(OH)D concentrations ≥ 40 ng/mL. In Part 2, the optimal regimen chosen from Part 1 was compared (2:1) to a standard-of-care control dose (600 international units [IU] daily) over 16 weeks. A final population pharmacokinetic model using both parts was developed to perform dosing simulations and determine important co-variates in the pharmacokinetics of vitamin D.
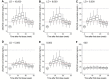
Results: Based on empiric and simulation data, the daily dose of 8000 IU and a loading dose of 50,000 IU were chosen; this regimen raised 25(OH)D concentrations above 40 ng/mL in the majority of participants while avoiding concentrations > 100 ng/mL. A 50,000-IU loading dose led to faster achievement of 25(OH)D therapeutic concentrations (≥ 40 ng/mL). The estimated median (5th-95th percentiles) apparent clearance of vitamin D from the final population pharmacokinetic model was 0.181 (0.155-0.206) L/h. The body mass index z-score was a significant covariate on apparent clearance and was associated with a significantly decreased median half-life in 25(OH)D (body mass index z-score 1.00-1.99: 97.7 days, body mass index z-score 2.00-2.99: 65.9 days, body mass index z-score ≥ 3.00: 39.1 days, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Obesity impacts vitamin D clearance and the half-life, but serum concentrations > 40 ng/mL can be reached in most children using a loading dose of 50,000 IU followed by a daily dose of 8000 IU.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier number NCT03686150.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jason E. Lang reports consulting fees from AbbVie, Inc. unrelated to the current project. Saranya Venkatachalam, Jessica Snowden, Laura James, Scott Bickel, J. Marc Majure, Rodrigo Gonzalez Ramirez, Brian O’Sullivan, and Christoph P. Hornik have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article. Stephen Balevic is a consultant for UCB and has received research funding from Purdu Pharma.
Figures



References
-
- Brehm JM, Schuemann B, Fuhlbrigge AL, Hollis BW, Strunk RC, Zeiger RS, Childhood Asthma Management Program Research Group et al. Serum vitamin D levels and severe asthma exacerbations in the Childhood Asthma Management Program study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(1):52–58.e55. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.03.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UG1 OD024945/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD030016/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024943/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024947/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024958/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024942/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024944/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024946/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024955/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024953/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024950/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024952/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024951/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024948/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024959/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD024957/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024954/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD030019/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 OD024956/OD/NIH HHS/United States

