Lewis Base-assisted Arylation of Unsaturated Carbonyls
- PMID: 37647146
- PMCID: PMC10947297
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202302490
Lewis Base-assisted Arylation of Unsaturated Carbonyls
Abstract
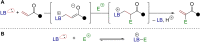
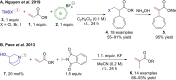
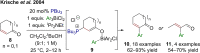
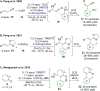
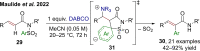
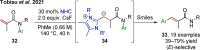
The combination of Lewis bases with α,β-unsaturated carbonyls allows the in-situ generation of enolates without the need for strong Brønsted bases. Recently developed synthetic methods employ this approach for arylation followed by elimination of the Lewis base, regenerating the alkene. This strategy has been deployed for formal α- or β-C-H arylation in different contexts, namely (a) transition metal catalysis, (b) rearrangement reactions utilizing hypervalent main group elements and (c) organocatalysis. This concept article provides an overview of the developed strategies, highlighting and contextualizing their features.
Keywords: C−C coupling; Lewis bases; aromatic substitution; organocatalysis; rearrangement.
© 2023 The Authors. Chemistry - A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- None
-
- Denmark S. E., Beutner G. L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1560–1638; - PubMed
-
- Vedejs E., Denmark S. E., Lewis Base Catalysis in Organic Synthesis, 3 Volume Set, Wiley & Sons, Limited, John, 2016.
-
- None
-
- Morita K.-I., Suzuki Z., Hirose H., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1968, 41, 2815;
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

