Cell-Type Composition Affects Adipose Gene Expression Associations With Cardiometabolic Traits
- PMID: 37647564
- PMCID: PMC10588284
- DOI: 10.2337/db23-0365
Cell-Type Composition Affects Adipose Gene Expression Associations With Cardiometabolic Traits
Abstract
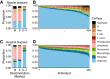
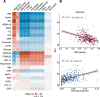
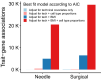
Understanding differences in adipose gene expression between individuals with different levels of clinical traits may reveal the genes and mechanisms leading to cardiometabolic diseases. However, adipose is a heterogeneous tissue. To account for cell-type heterogeneity, we estimated cell-type proportions in 859 subcutaneous adipose tissue samples with bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) using a reference single-nuclear RNA-seq data set. Cell-type proportions were associated with cardiometabolic traits; for example, higher macrophage and adipocyte proportions were associated with higher and lower BMI, respectively. We evaluated cell-type proportions and BMI as covariates in tests of association between >25,000 gene expression levels and 22 cardiometabolic traits. For >95% of genes, the optimal, or best-fit, models included BMI as a covariate, and for 79% of associations, the optimal models also included cell type. After adjusting for the optimal covariates, we identified 2,664 significant associations (P ≤ 2e-6) for 1,252 genes and 14 traits. Among genes proposed to affect cardiometabolic traits based on colocalized genome-wide association study and adipose expression quantitative trait locus signals, 25 showed a corresponding association between trait and gene expression levels. Overall, these results suggest the importance of modeling cell-type proportion when identifying gene expression associations with cardiometabolic traits.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL129982/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL154730/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007092/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK126185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010505/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM135123/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

