Brazilian Society of Otology task force - Otosclerosis: evaluation and treatment
- PMID: 37647735
- PMCID: PMC10474207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2023.101303
Brazilian Society of Otology task force - Otosclerosis: evaluation and treatment
Abstract
Objectives: To review and provide evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of otosclerosis.
Methods: Task force members were educated on knowledge synthesis methods, including electronic database search, review and selection of relevant citations, and critical appraisal of selected studies. Articles written in English or Portuguese on otosclerosis were eligible for inclusion. The American College of Physicians' guideline grading system and the American Thyroid Association's guideline criteria were used for critical appraisal of evidence and recommendations for therapeutic interventions.
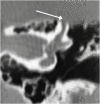
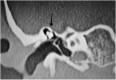
Results: The topics were divided into 2 parts: 1) Diagnosis - audiologic and radiologic; 2) Treatment - hearing AIDS, pharmacological therapy, stapes surgery, and implantable devices - bone-anchored devices, active middle ear implants, and Cochlear Implants (CI).
Conclusions: The pathophysiology of otosclerosis has not yet been fully elucidated, but environmental factors and unidentified genes are likely to play a significant role in it. Women with otosclerosis are not at increased risk of worsening clinical condition due to the use of contraceptives or during pregnancy. Drug treatment has shown little benefit. If the patient does not want to undergo stapedotomy, the use of hearing aids is well indicated. Implantable systems should be indicated only in rare cases, and the CI should be indicated in cases of profound deafness.
Keywords: Hearing loss, conductive; Hearing loss, mixed conductive-sensorineural; Otosclerosis; Stapes surgery.
Copyright © 2023 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier España S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures














References
-
- Foster M.F., Backous D.D. Clinical evaluation of the patient with otosclerosis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2018;51:319–326. - PubMed
-
- Markou K., Goudakos J. An overview of the etiology of otosclerosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Iyer P.V., Gristwood R.E. Histopathology of the stapes in otosclerosis. Pathology. 1984;16:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Clayton A.E., Mikulec A.A., Mikulec K.H., Merchant S.N., McKenna M.J. Association between osteoporosis and otosclerosis in women. J Laryngol Otol. 2004;118:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Quesnel A.M., Ishai R., McKenna M.J. Otosclerosis: temporal bone pathology. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2018;51:291–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

