Calculated Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level is A Predominant Predictor for New Onset of Ischemic Heart Disease
- PMID: 37648520
- PMCID: PMC10918049
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.64369
Calculated Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level is A Predominant Predictor for New Onset of Ischemic Heart Disease
Abstract
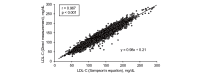
Aim: A high level of directly measured small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (sdLDL-C) is a strong risk factor for ischemic heart disease (IHD). However, it remains unclear whether estimated sdLDL-C level is a predictor for IHD. We investigated the associations of new onset of IHD with levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-HDL-C, triglycerides (TG), LDL-C and calculated sdLDL-C by Sampson's equation.
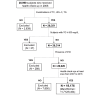
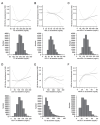
Methods: After exclusion of subjects with IHD or those with TG ≥ 800 mg/dL, a total of 18,176 subjects (men/women: 11,712/6,464, mean age: 46 years) were recruited among 28,990 Japanese individuals who received annual health checkups.
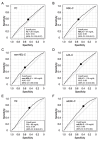
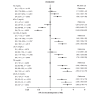
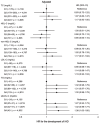
Results: During the 10-year follow-up period, 456 men (3.9%) and 121 women (1.9%) newly developed IHD. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard analyses after adjustment of age, sex, obesity, smoking habit, family history of IHD, estimated glomerular filtration rate, hypertension and diabetes mellitus at baseline showed that the hazard ratio (HR) (1.38 [95% confidence interval: 1.03-1.85]) for new onset of IHD in subjects with the 4th quartile (Q4) of sdLDL-C (≥ 42 mg/dL) was significantly higher than that in subjects with the 1st quartile (Q1) (≤ 24 mg/dL) as the reference, though the adjusted HRs in subjects with Q2-Q4 of TC, HDL-C, non-HDL-C, LDL-C and TG were comparable with those in subjects with Q1 of the respective lipid fractions. The adjusted HR with a restricted cubic spline increased with a higher level of calculated sdLDL-C as a continuous value at baseline.
Conclusions: sdLDL-C level calculated by Sampson's equation is a predominant predictor for the development of IHD in a general Japanese population.
Keywords: Ischemic heart disease; Small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Visseren FLJ, Mach F, Smulders YM, Carballo D, Koskinas KC, Back M, Benetos A, Biffi A, Boavida JM, Capodanno D, Cosyns B, Crawford C, Davos CH, Desormais I, Di Angelantonio E, Franco OH, Halvorsen S, Hobbs FDR, Hollander M, Jankowska EA, Michal M, Sacco S, Sattar N, Tokgozoglu L, Tonstad S, Tsioufis KP, van Dis I, van Gelder IC, Wanner C, Williams B, Societies ESCNC, Group ESCSD: 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J, 2021; 42: 3227-3337
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, Braun LT, de Ferranti S, Faiella-Tommasino J, Forman DE, Goldberg R, Heidenreich PA, Hlatky MA, Jones DW, Lloyd-Jones D, Lopez-Pajares N, Ndumele CE, Orringer CE, Peralta CA, Saseen JJ, Smith SC, Jr., Sperling L, Virani SS, Yeboah J: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation, 2019; 139: e1046-e1081 - PubMed
-
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, Chapman MJ, De Backer GG, Delgado V, Ference BA, Graham IM, Halliday A, Landmesser U, Mihaylova B, Pedersen TR, Riccardi G, Richter DJ, Sabatine MS, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Wiklund O, Group ESCSD: 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J, 2020; 41: 111-188 - PubMed
-
- Berneis KK, Krauss RM: Metabolic origins and clinical significance of LDL heterogeneity. J Lipid Res, 2002; 43: 1363-1379 - PubMed
-
- Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS: Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem, 1972; 18: 499-502 - PubMed

