Neutralization, effector function and immune imprinting of Omicron variants
- PMID: 37648855
- PMCID: PMC10511321
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06487-6
Neutralization, effector function and immune imprinting of Omicron variants
Abstract
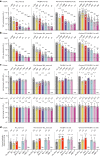
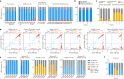
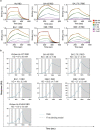
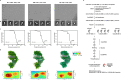
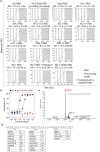
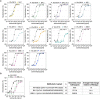
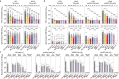
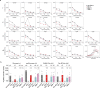
Currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants have acquired convergent mutations at hot spots in the receptor-binding domain1 (RBD) of the spike protein. The effects of these mutations on viral infection and transmission and the efficacy of vaccines and therapies remains poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that recently emerged BQ.1.1 and XBB.1.5 variants bind host ACE2 with high affinity and promote membrane fusion more efficiently than earlier Omicron variants. Structures of the BQ.1.1, XBB.1 and BN.1 RBDs bound to the fragment antigen-binding region of the S309 antibody (the parent antibody for sotrovimab) and human ACE2 explain the preservation of antibody binding through conformational selection, altered ACE2 recognition and immune evasion. We show that sotrovimab binds avidly to all Omicron variants, promotes Fc-dependent effector functions and protects mice challenged with BQ.1.1 and hamsters challenged with XBB.1.5. Vaccine-elicited human plasma antibodies cross-react with and trigger effector functions against current Omicron variants, despite a reduced neutralizing activity, suggesting a mechanism of protection against disease, exemplified by S309. Cross-reactive RBD-directed human memory B cells remained dominant even after two exposures to Omicron spikes, underscoring the role of persistent immune imprinting.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.P., M. Beltramello, B.G., H.D., J.B., C.S.-F., F.M., M.D., D.P., L.V., C. Saliba, M.G., G. Lombardo, G. Leoni, C.M., E.D., A.R., R.A., D.J., S.S., K.C., E.C., G. Schnell, J.Z., N. Farhat, D.B., J.N., A. Chen, F.A.L., N.C., M.A.S., L.E.R., A.C., L.A.P., G. Saliba, A.L. and D.C. are employees of and may hold shares in Vir Biotechnology. L.A.P. is a former employee and shareholder of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and is member of the scientific advisory board of AI-driven Structure-enabled Antiviral Platform (ASAP). Regeneron provided no funding for this work. M.S.D. is a consultant for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology, Senda Biosciences, Generate Biomedicines, Moderna and Immunome. D.V. is an inventor on patent applications 14/930,792, PCT/US2019/020029, 63/132,863 and PCT/US2021/017799 held or submitted by the University of Washington related to RBD-based nanoparticle vaccines. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Moderna and Emergent BioSolutions. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

