Metabolic programs of T cell tissue residency empower tumour immunity
- PMID: 37648857
- PMCID: PMC11238873
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06483-w
Metabolic programs of T cell tissue residency empower tumour immunity
Abstract
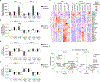
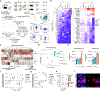
Tissue resident memory CD8+ T (TRM) cells offer rapid and long-term protection at sites of reinfection1. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes with characteristics of TRM cells maintain enhanced effector functions, predict responses to immunotherapy and accompany better prognoses2,3. Thus, an improved understanding of the metabolic strategies that enable tissue residency by T cells could inform new approaches to empower immune responses in tissues and solid tumours. Here, to systematically define the basis for the metabolic reprogramming supporting TRM cell differentiation, survival and function, we leveraged in vivo functional genomics, untargeted metabolomics and transcriptomics of virus-specific memory CD8+ T cell populations. We found that memory CD8+ T cells deployed a range of adaptations to tissue residency, including reliance on non-steroidal products of the mevalonate-cholesterol pathway, such as coenzyme Q, driven by increased activity of the transcription factor SREBP2. This metabolic adaptation was most pronounced in the small intestine, where TRM cells interface with dietary cholesterol and maintain a heightened state of activation4, and was shared by functional tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in diverse tumour types in mice and humans. Enforcing synthesis of coenzyme Q through deletion of Fdft1 or overexpression of PDSS2 promoted mitochondrial respiration, memory T cell formation following viral infection and enhanced antitumour immunity. In sum, through a systematic exploration of TRM cell metabolism, we reveal how these programs can be leveraged to fuel memory CD8+ T cell formation in the context of acute infections and enhance antitumour immunity.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.W.G. serves on the scientific advisory boards of ArsenalBio and Foundery Innovations. H.C. is a consultant for Kumquat Biosciences. M.F.K. is a founder and shareholder of PIONYR Immunotherapeutic and Foundery Innovations. A provisional patent application has been filed by M.R-C., G.G, and A.G. covering the methods of use of
Figures


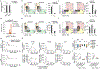








References
-
- Park SL, Gebhardt T & Mackay LK Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells in Cancer Immunosurveillance. Trends Immunol 40, 735–747 (2019). - PubMed
Methods References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD021815/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157710/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA030199/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL146358/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150282/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA256133/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072117/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI052116/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA197363/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI067545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI132122/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

