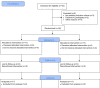
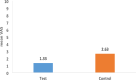
Omega-3 nanoemulgel in prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis and its associated effect on microbiome: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 37648997
- PMCID: PMC10470147
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03276-5
Omega-3 nanoemulgel in prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis and its associated effect on microbiome: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Oral mucositis (OM) is recognized as one of the most frequent debilitating sequelae encountered by head and neck cancer (HNC) patients treated by radiotherapy. This results in severe mucosal tissue inflammation and oral ulcerations that interfere with patient's nutrition, quality of life (QoL) and survival. Omega-3 (ω-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have recently gained special interest in dealing with oral diseases owing to its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and wound healing properties. Thus, this study aims to assess topical Omega-3 nanoemulgel efficacy in prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis and regulation of oral microbial dysbiosis.
Materials and methods: Thirty-four head and neck cancer patients planned to receive radiotherapy were randomly allocated into two groups: Group I: conventional preventive treatment and Group II: topical Omega-3 nanoemulgel. Patients were evaluated at baseline, three and six weeks after treatment using the World Health Organization (WHO) grading system for oral mucositis severity, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for perceived pain severity, and MD-Anderson Symptom Inventory for Head and Neck cancer (MDASI-HN) for QoL. Oral swabs were collected to assess oral microbiome changes.
Results: VAS scores and WHO mucositis grades were significantly lower after six weeks of treatment with topical Omega-3 nanoemulgel when compared to the conventional treatment. The total MDASI score was significantly higher in the control group after three weeks of treatment, and the head and neck subscale differed significantly at both three and six weeks. A significant reduction in Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was observed after six weeks in the test group indicating less microbial dysbiosis.
Conclusions: Topical Omega-3 nanoemulgel demonstrated a beneficial effect in prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis with a possibility of regulating oral microbial dysbiosis.
Keywords: Microbiome; Nanoemulgel; Omega-3; Oral mucositis; Prevention.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probiotics in the management of radiation-induced oral mucositis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 18;14:1477143. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1477143. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39359935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of photobiomodulation on the severity of oral mucositis and molecular changes in head and neck cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy: a study protocol for a cost-effectiveness randomized clinical trial.Trials. 2019 Feb 1;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3196-8. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30709370 Free PMC article.
-
The M. D. Anderson symptom inventory-head and neck module, a patient-reported outcome instrument, accurately predicts the severity of radiation-induced mucositis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 Dec 1;72(5):1355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.02.072. Epub 2008 May 22. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 18501527
-
Effect of low-level laser therapy on patient reported measures of oral mucositis and quality of life in head and neck cancer patients receiving chemoradiotherapy--a randomized controlled trial.Support Care Cancer. 2013 May;21(5):1421-8. doi: 10.1007/s00520-012-1684-4. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Support Care Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23224689 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of the microbiome on radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis and its management: A comprehensive review.Oral Oncol. 2023 Sep;144:106488. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106488. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Oral Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37399707 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukopenia, weight loss and oral mucositis induced by 5-Fluorouracil in hamsters' model: A regenerative approach using electrospun poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) membrane.Oncotarget. 2025 Feb 18;16:103-117. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28685. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 39969203 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Treatments for Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer.Cureus. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):e86145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86145. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40671993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of oral dysbiosis and HPV infection in head and neck cancer: from molecular and cellular mechanisms to early diagnosis and therapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 18;13:1273516. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1273516. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38179168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakr IS, Zaki AM, El-Moslemany RM, Elsaka RO. Vitamin D oral gel for prevention of radiation‐induced oral mucositis: a randomized clinical trial. Oral Dis. 2020;:odi13650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources