Berberine improves inhibitory avoidance memory impairment of Toxoplasma gondii-infected rat model of ketamine-induced schizophrenia
- PMID: 37649038
- PMCID: PMC10469906
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04107-4
Berberine improves inhibitory avoidance memory impairment of Toxoplasma gondii-infected rat model of ketamine-induced schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Memory impairment caused by Toxoplasma gondii infection has been documented. Berberine (BRB) is well known for its enhancing effects on memory and has shown promising results. However, the impact of BRB on T. gondii infection and schizophrenia-induced consolidation and reconsolidation memory impairment is still unclear. Here; we examined the effect of BRB on the inhibitory avoidance (IA) memory consolidation and reconsolidation impairment induced by T. gondii infection, and ketamine (Ket) as a pharmacological model of schizophrenia. Also; the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampus were analyzed.
Methods: Rats were infected with T. gondii RH strain or received Ket (30 mg/kg/day) intraperitoneally (i.p) for at least five consecutive days (as the model of schizophrenia). Then followed by oral administration with BRB (25 mg/kg/day) for five days. Finally, the IA memory retention test was examined 48 post-conditioning, and BDNF was measured.
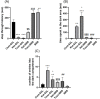
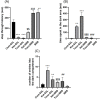
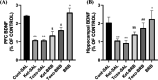
Results: Results indicated IA memory impairment in T. gondii-infected animals since lower step-through latency (STL) was observed than in control animals. We found significant (P = 0.01, P = 0.001) elevations in STL and a significant decrease (P = 0.001) in total time spent in the dark area following BRB administration in infected and Ket-treated rats, indicating improvement (increased STL) in consolidation and reconsolidation memory. Moreover, BDNF levels were reduced (P = 0.01) in the hippocampus and mPFC regions of both T. gondii- infected and Ket-induced groups, which remarkably enhanced after BRB treatment. Furthermore; we found that BRB administration notably increased the mPFC BDNF levels in mPFC (P < 0.01) and hippocampus (P = 0.001) in the Ket-treated and rats infected with T. gondii.
Conclusion: Taken together; BRB may be a valuable preclinical treatment for improving memory impairment through BDNF expression in PFC and hippocampus, therefore; BRB is suggested for memory disturbances induced by T. gondii infection.
Keywords: Berberine; Consolidation; Inhibitory avoidance memory; Reconsolidation; Schizophrenia rat model; Toxoplasma gondii.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
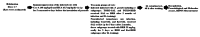

Similar articles
-
Involvement of GABAergic, BDNF and Nox-2 mechanisms in the prevention and reversal of ketamine-induced schizophrenia-like behavior by morin in mice.Brain Res Bull. 2018 May;139:292-306. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 29548911
-
Binge and Subchronic Exposure to Ketamine Promote Memory Impairments and Damages in the Hippocampus and Peripheral Tissues in Rats: Gallic Acid Protective Effects.Neurotox Res. 2020 Aug;38(2):274-286. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00215-y. Epub 2020 May 26. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 32458406
-
Alpha-lipoic acid alone and combined with clozapine reverses schizophrenia-like symptoms induced by ketamine in mice: Participation of antioxidant, nitrergic and neurotrophic mechanisms.Schizophr Res. 2015 Jul;165(2-3):163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Schizophr Res. 2015. PMID: 25937462
-
[Toxoplasma gondii: a potential role in the genesis of psychiatric disorders].Encephale. 2013 Feb;39(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23095600 Review. French.
-
Toxoplasma gondii and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: an animal model perspective.Schizophr Bull. 2012 Nov;38(6):1155-61. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbs079. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Schizophr Bull. 2012. PMID: 22941742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing Ischemic Stroke Diagnosis and Treatment: The Promising Role of Neurovascular Unit-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 20;14(3):378. doi: 10.3390/biom14030378. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tailoring Risperidone-Loaded Glycethosomal In Situ Gels Using Box-Behnken Design for Treatment of Schizophrenia-Induced Rats via Intranasal Route.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 24;15(11):2521. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112521. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004501 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on antidepressant effects and mechanisms of berberine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1331440. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1331440. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38318145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular identification, risk factors' assessment and phylogenetic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii in goats from Malakand Division, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Jun 10;49(4):217. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10783-z. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40493124
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) changes in rodent models of schizophrenia induced by ketamine: a systematic review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8111-8124. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03912-7. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39976721
References
-
- Pappas G, Roussos N, Falagas ME. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39(12):1385–94. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Azu B, et al. Neuroprotective effects of the ethanol stem bark extracts of Terminalia ivorensis in ketamine-induced schizophrenia-like behaviors and oxidative damage in mice. Pharm Biol. 2016;54(12):2871–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

