Effects of dysregulated glucose metabolism on the occurrence and ART outcome of endometriosis
- PMID: 37649072
- PMCID: PMC10466766
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01280-7
Effects of dysregulated glucose metabolism on the occurrence and ART outcome of endometriosis
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is associated with systemic metabolic indicators, including body mass index (BMI), glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism, while the association between metabolic indexes and the occurrence and assisted reproductive technology (ART) outcome of endometriosis is unclear. We aimed to evaluate the characteristics of systemic metabolic indexes of endometriosis patients with infertility and their effects on pregnancy outcome after ART treatment.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study involve 412 endometriosis patients and 1551 controls was conducted. Primary outcome was metabolic indexes, and secondary measures consisted of the influence of metabolic indexes on the number of retrieved oocytes and ART outcomes.
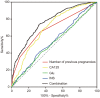
Results: Endometriosis patients had higher insulin (INS) [6.90(5.10-9.50) vs 6.50(4.80-8.90) μU/mL, P = 0.005]. A prediction model for endometriosis combining the number of previous pregnancies, CA125, fasting blood glucose (Glu) and INS, had a sensitivity of 73.9%, specificity of 67.8% and area under curve (AUC) of 0.77. There were no significant differences in ART outcomes and complications during pregnancy. The serum levels of Glu before pregnancy were associated with GDM both in endometriosis group (aOR 12.95, 95% CI 1.69-99.42, P = 0.014) and in control group (aOR 4.15, 95% CI 1.50-11.53, P = 0.006).
Conclusions: We found serum Glu is related to the number of retrieved oocytes in control group, serum INS is related to the number of retrieved oocytes in endometriosis group, while serum Glu and INS before pregnancy are related to the occurrence of GDM in two groups. A prediction model based on metabolic indexes was established, representing a promising non-invasive method to predict endometriosis patients with known pregnancy history.
Keywords: ART outcomes; Endometriosis; GDM; Metabolic indicator; Number of retrieved oocytes.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Younis JS, Shapso N, Fleming R, Ben-Shlomo I, Izhaki I. Impact of unilateral versus bilateral ovarian endometriotic cystectomy on ovarian reserve: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2019;25(3):375–391. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery GW, Giudice LC. New lessons about endometriosis—somatic mutations and disease heterogeneity. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(19):1881–1882. - PubMed
-
- Shafrir AL, Farland LV, Shah DK, Harris HR, Kvaskoff M, Zondervan K, et al. Risk for and consequences of endometriosis: a critical epidemiologic review. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;51:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Zondervan KT, Becker CM, Missmer SA. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(13):1244–1256. - PubMed
-
- Ortona E, Pierdominici M, Maselli A, Veroni C, Aloisi F, Shoenfeld Y. Sex-based differences in autoimmune diseases. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2016;52(2):205–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous