Correlations between IL-36 family cytokines in peripheral blood and subjective and objective assessment results in patients with allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 37649097
- PMCID: PMC10470177
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-023-00834-y
Correlations between IL-36 family cytokines in peripheral blood and subjective and objective assessment results in patients with allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-36 family cytokines have received increasing attention, especially in the fields of inflammation and immunity research. However, whether IL-36 family cytokine levels are correlated with the results of the assessment of allergic rhinitis (AR) and affect the severity of AR remains unknown. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the correlations between IL-36 family cytokine levels and subjective and objective assessment results and to further analyze the possible mechanisms of IL-36 family cytokines in the development of AR.
Methods: An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the concentrations of the IL-36 family cytokines IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, IL-36Ra, and IL-38 in the peripheral blood of patients with AR. The condition of patients with AR was assessed by 22-item sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT-22) score, visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for disease severity, and serum inhalant allergen immunoglobulin E (IgE) detection. Correlations between IL-36 family cytokine levels and subjective and objective assessment results in patients with AR were analyzed.
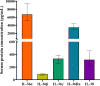
Results: The concentration of IL-36α in the peripheral blood of patients with AR was the highest, and the concentration of IL-36β was the lowest. The concentration of IL-36α was higher in juvenile patients than in adult patients, and there was a difference in the IL-36Ra level between the perennial allergen group and the seasonal allergen group. There was a positive correlation between IL-36α level and IL-36γ level, IL-36γ level and IL-36Ra level, and IL-36Ra level and IL-38 level, and IL-36β level was positively correlated with IL-36Ra and IL-38 levels, respectively. IL-36α level was positively correlated with VAS score for nasal congestion symptom. IL-36β level was positively correlated with the total VAS score for ocular symptoms and VAS scores for ocular itching and eye pain symptoms. However, there was no correlation between the levels of all cytokines in IL-36 family and SNOT-22 score, the number of positive inhaled allergens, or the highest positive intensity of allergen specific immunoglobulin E (sIgE).
Conclusion: Peripheral blood IL-36 family cytokines play an important role in AR, and the concentrations of IL-36α and IL-36β were related to the severity of symptoms in patients with AR.
Keywords: Allergens; Allergic rhinitis; Interleukin-36; Symptom assessment.
© 2023. Canadian Society of Allergy & Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Altered serum levels of IL-36 cytokines (IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, and IL-36Ra) and their potential roles in Guillain-Barré syndrome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 24;99(52):e23832. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023832. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33350771 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of IL-36 cytokines in folliculitis and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.Australas J Dermatol. 2020 Feb;61(1):e39-e45. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13143. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Australas J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31424098
-
Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 9;286(49):42594-42602. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.267922. Epub 2011 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21965679 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of New IL-1 Family Members (IL-36 and IL-38) in Atopic Dermatitis, Allergic Asthma, and Allergic Rhinitis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020 Jun 12;20(8):40. doi: 10.1007/s11882-020-00937-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020. PMID: 32533268 Review.
-
Biology of IL-36 cytokines and their role in disease.Semin Immunol. 2013 Dec 15;25(6):458-65. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24355486 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of serum IL-36 subfamily cytokines on clinical manifestations of asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2025 Jan 18;4(2):100419. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2025.100419. eCollection 2025 May. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2025. PMID: 40115968 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Airway Epithelial-Derived Alarmins in Asthma: Perspectives for Therapeutic Targets.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 11;12(10):2312. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102312. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

