The characteristics and medical applications of antler stem cells
- PMID: 37649124
- PMCID: PMC10468909
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03456-8
The characteristics and medical applications of antler stem cells
Abstract
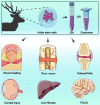
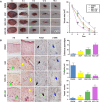
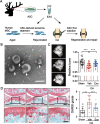
Antlers are the only fully regenerable mammalian appendages whose annual renewal is initiated by antler stem cells (ASCs), defined as a specialized type of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with embryonic stem cell properties. ASCs possess the same biological features as MSCs, including the capacity for self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, immunomodulatory functions, and the maintenance of stem cell characteristics after multiple passages. Several preclinical studies have shown that ASCs exhibit promising potential in wound healing, bone repair, osteoarthritis, anti-tissue fibrosis, anti-aging, and hair regeneration. Medical applications based on ASCs and ASC-derived molecules provide a new source of stem cells and therapeutic modalities for regenerative medicine. This review begins with a brief description of antler regeneration and the role of ASCs. Then, the properties and advantages of ASCs are described. Finally, medical research advances regarding ASCs are summarized, and the prospects and challenges of ASCs are highlighted.
Keywords: Antler; Medical applications; Stem cells.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- De Luca M, Aiuti A, Cossu G, Parmar M, Pellegrini G, Robey PG. Advances in stem cell research and therapeutic development. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(7):801–811. - PubMed
-
- Bacakova L, Zarubova J, Travnickova M, Musilkova J, Pajorova J, Slepicka P, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells—a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(4):1111–1126. - PubMed
-
- Kuo YR, Wang CT, Cheng JT, Kao GS, Chiang YC, Wang CJ. Adipose-derived stem cells accelerate diabetic wound healing through the induction of autocrine and paracrine effects. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(1):71–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

