Impaired resolution of blood transcriptomes through tuberculosis treatment with diabetes comorbidity
- PMID: 37649224
- PMCID: PMC10468587
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.1375
Impaired resolution of blood transcriptomes through tuberculosis treatment with diabetes comorbidity
Abstract
Background: People with diabetes are more likely to develop tuberculosis (TB) and to have poor TB-treatment outcomes than those without. We previously showed that blood transcriptomes in people with TB-diabetes (TB-DM) co-morbidity have excessive inflammatory and reduced interferon responses at diagnosis. It is unknown whether this persists through treatment and contributes to the adverse outcomes.
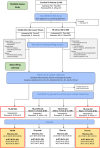
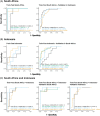
Methods: Pulmonary TB patients recruited in South Africa, Indonesia and Romania were classified as having TB-DM, TB with prediabetes, TB-related hyperglycaemia or TB-only, based on glycated haemoglobin concentration at TB diagnosis and after 6 months of TB treatment. Gene expression in blood at diagnosis and intervals throughout treatment was measured by unbiased RNA-Seq and targeted Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification. Transcriptomic data were analysed by longitudinal mixed-model regression to identify whether genes were differentially expressed between clinical groups through time. Predictive models of TB-treatment response across groups were developed and cross-tested.
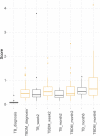
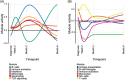
Results: Gene expression differed between TB and TB-DM patients at diagnosis and was modulated by TB treatment in all clinical groups but to different extents, such that differences remained in TB-DM relative to TB-only throughout. Expression of some genes increased through TB treatment, whereas others decreased: some were persistently more highly expressed in TB-DM and others in TB-only patients. Genes involved in innate immune responses, anti-microbial immunity and inflammation were significantly upregulated in people with TB-DM throughout treatment. The overall pattern of change was similar across clinical groups irrespective of diabetes status, permitting models predictive of TB treatment to be developed.
Conclusions: Exacerbated transcriptome changes in TB-DM take longer to resolve during TB treatment, meaning they remain different from those in uncomplicated TB after treatment completion. This may indicate a prolonged inflammatory response in TB-DM, requiring prolonged treatment or host-directed therapy for complete cure. Development of transcriptome-based biomarker signatures of TB-treatment response should include people with diabetes for use across populations.
Keywords: diabetes; transcriptome; treatment; tuberculosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
G. W. holds patents about methods of tuberculosis diagnosis and tuberculosis biomarkers which are unrelated to the current study. No other authors have any declared conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Koesoemadinata RC, Mcallister SM, Soetedjo NNM, et al. Latent TB infection and pulmonary TB disease among patients with diabetes mellitus in Bandung, Indonesia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017;111:81‐89. - PubMed
-
- Noubiap JJ, Nansseu JR, Nyaga UF, et al. Global prevalence of diabetes in active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of data from 2.3 million patients with tuberculosis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e448‐e460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
