What role does PDL1 play in EMT changes in tumors and fibrosis?
- PMID: 37649487
- PMCID: PMC10463740
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1226038
What role does PDL1 play in EMT changes in tumors and fibrosis?
Abstract
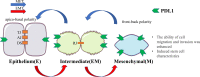
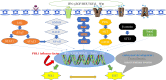
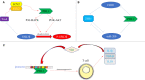
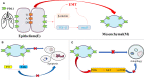
Epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) plays a pivotal role in embryonic development, tissue fibrosis, repair, and tumor invasiveness. Emerging studies have highlighted the close association between EMT and immune checkpoint molecules, particularly programmed cell death ligand 1 (PDL1). PDL1 exerts its influence on EMT through bidirectional regulation. EMT-associated factors, such as YB1, enhance PDL1 expression by directly binding to its promoter. Conversely, PDL1 signaling triggers downstream pathways like PI3K/AKT and MAPK, promoting EMT and facilitating cancer cell migration and invasion. Targeting PDL1 holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for EMT-related diseases, including cancer and fibrosis. Indeed, PDL1 inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have shown promising results in clinical trials for various cancers. Recent research has also indicated their potential benefit in fibrosis treatment in reducing fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix deposition, thereby addressing fibrosis. In this review, we examine the multifaceted role of PDL1 in immunomodulation, growth, and fibrosis promotion. We discuss the challenges, mechanisms, and clinical observations related to PDL1, including the limitations of the PD1/PDL1 axis in treatment and PD1-independent intrinsic PDL1 signaling. Our study highlights the dynamic changes in PDL1 expression during the EMT process across various tumor types. Through interplay between PDL1 and EMT, we uncover co-directional alterations, regulatory pathways, and diverse changes resulting from PDL1 intervention in oncology. Additionally, our findings emphasize the dual role of PDL1 in promoting fibrosis and modulating immune responses across multiple diseases, with potential implications for therapeutic approaches. We particularly investigate the therapeutic potential of targeting PDL1 in type II EMT fibrosis: strike balance between fibrosis modulation and immune response regulation. This analysis provides valuable insights into the multifaceted functions of PDL1 and contributes to our understanding of its complex mechanisms and therapeutic implications.
Keywords: EMT-related disease; epithelial-mesenchymal transformation; fibrosis; immune escape; programmed death-ligand 1.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Zhao and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

